ASTM A178 steel tubes are electrical resistance welded (ERW) tubes of carbon and carbon-manganese steel used as boiler tubes, boiler flues, superheater flues, and safety ends.
It is suitable for steel tubes with an outside diameter of 12.7-127mm and a wall thickness between 0.9-9.1mm.
ASTM A178 tubes are suitable for resistance welded tubes with outside diameters between 1/2 - 5 in [12.7 - 127 mm] and wall thicknesses between 0.035 - 0.360 in [0.9 - 9.1 mm], although other sizes are of course available as required, provided that these tubes meet all other requirements of this specification.
There are three grades to cope with different usage environments.
Grade A, Grade C, and Grade D.
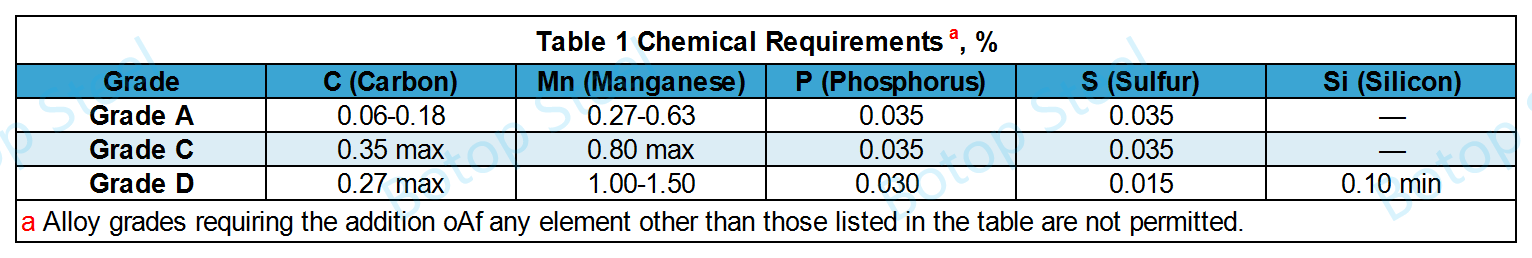
| Grade | Carbon Steel Type |
| Grade A | Low-Carbon Steel |
| Grade C | Medium-Carbon Steel |
| Grade D | Carbon-Manganese Steel |
Material furnished under this specification shall conform to the applicable requirements of the current edition of Specification A450/A450M. unless otherwise provided herein.
Grade A and Grade C do not specify a specific steel; select the appropriate raw material as needed.
The steel for Grade D shall be killed.
Killed steel is produced by adding deoxidizers (e.g., silicon, aluminum, manganese, etc.) to molten steel during the steel production process, thereby reducing or eliminating the oxygen content of the steel.
This treatment improves the homogeneity and stability of the steel, enhances its mechanical properties, and improves corrosion resistance.
Killed steels are therefore widely used in applications where a high degree of homogeneity and excellent mechanical properties are required, such as the manufacture of pressure vessels, boilers, and large structural components.
The steel tubes are manufactured using the ERW manufacturing process.
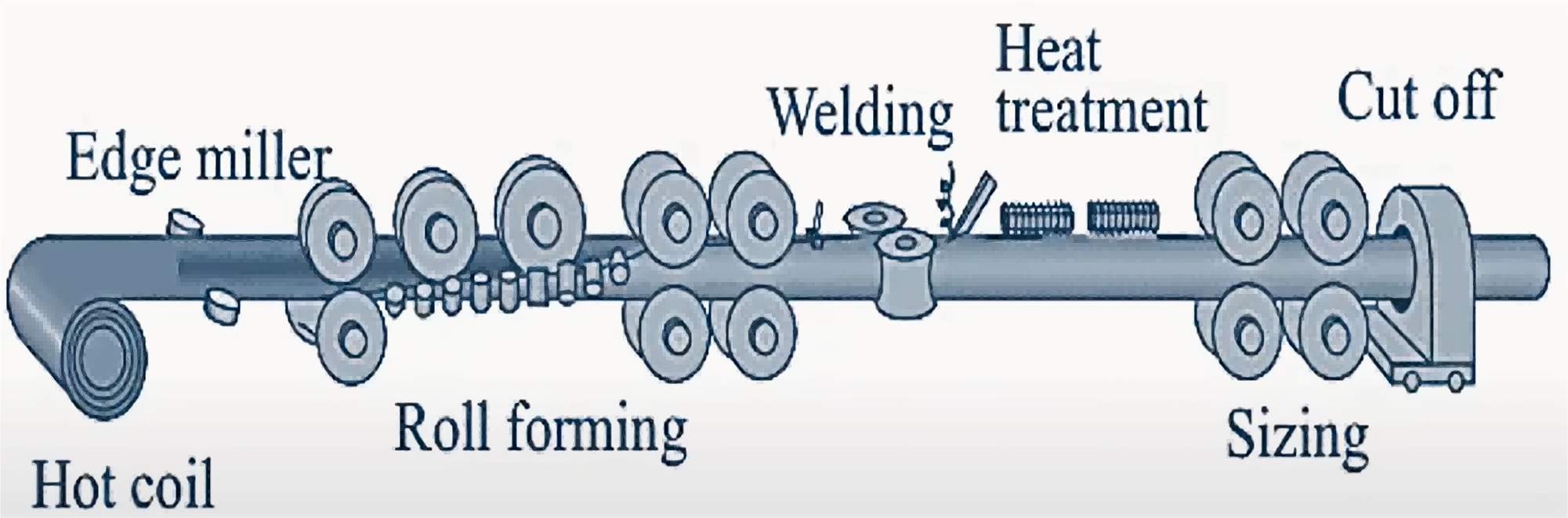
ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) is a process ideally suited for manufacturing carbon steel pipe.
With the advantages of high welding strength, smooth internal and external surfaces, fast production speed, and low price, it is widely used in many industrial and construction fields.
ASTM A178 steel pipe must be heat treated during the manufacturing process. It is used to improve the mechanical properties and structural stability of the pipe, as well as to eliminate stresses that may have been introduced during the welding process.
After welding, all tubes shall be heat treated at a temperature of 1650°F [900°C] or higher and followed by cooling in air or in the cooling chamber of a controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Cold-drawn tubes shall be heat treated after the final cold-draw pass at a temperature of 1200°F [650°C] or higher.
When product analysis is performed, the frequency of inspection is determined as follows.
| Classification | Inspection Frequency |
| Outer diameter ≤ 3in [76.2mm] | 250 pcs/time |
| Outer diameter > 3in [76.2mm] | 100 pcs/time |
| Distinguish by tube heat number | Per heat number |
Mechanical property requirements do not apply to tubing smaller than 1/8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter or 0.015 in. [0.4 mm] in thickness.
1. Tensile Property
For Classes C and D, a tensile test shall be performed on two tubes in each lot.
For Grade A tubing, tensile testing is not normally required. This is due to the fact that Grade A tubing is primarily used for low-pressure and low-temperature applications.
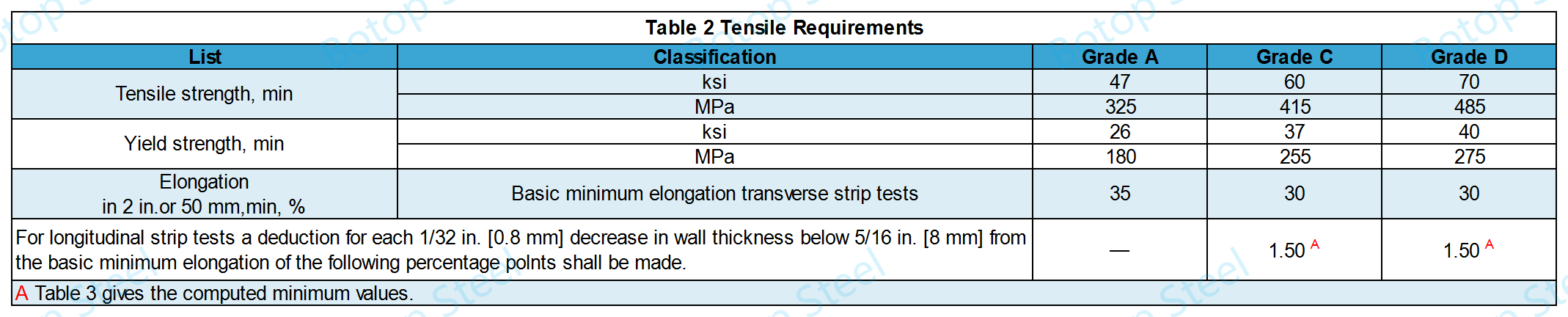
Table 3 gives the computed minimum elongation values for each 1/32 in. [0.8 mm] decrease in wall thickness.
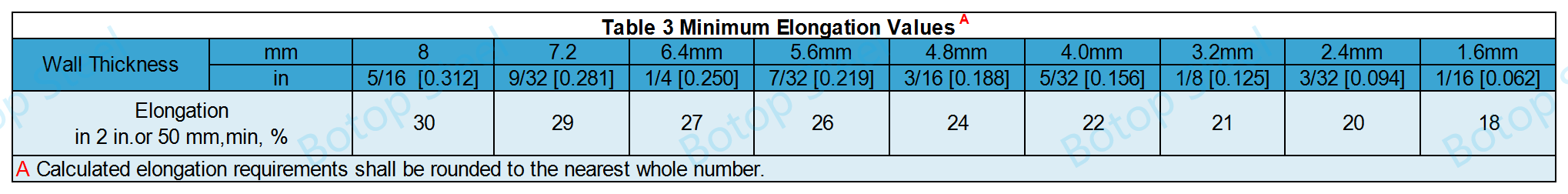
If the wall thickness of the steel pipe is not one of these wall thicknesses, it can also be calculated by the formula.
Inch Units: E = 48t + 15.00 or ISI Units: E = 1.87t + 15.00
E = elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, %,
t= actual specimen thickness, in. [mm].
2. Crush Test
Extrusion tests are performed on pipe sections 2 1/2 inches [63 mm] in length which must withstand longitudinal extrusion without cracking, splitting, or splitting at the welds.

For tubing less than 1 in. [25.4 mm] in outside diameter, the length of the specimen shall be 2 1/2 times the outside diameter of the tube. Slight surface checks shall not be cause for rejection.
3. Flattening Test
The experimental method conforms to the relevant requirements of ASTM A450 Section 19.
4. Flange Test
The experimental method conforms to the relevant requirements of ASTM A450 Section 22.
5. Reverse Flattening Test
The experimental method conforms to the relevant requirements of ASTM A450, Section 20.
Hydrostatic or non-destructive electrical testing is performed on each steel pipe.
Requirements are in accordance with ASTM A450, Section 24 or 26.
The following data is derived from ASTM A450 and meets the relevant requirements for welded steel pipe only.
Weight Deviation
0 - +10%.
Wall Thickness Deviation
0 - +18%.
Outside Diameter Deviation
| Outside Diameter | Permissible Variations | ||
| in | mm | in | mm |
| OD ≤1 | OD≤ 25.4 | ±0.004 | ±0.1 |
| 1<OD ≤1½ | 25.4<OD ≤38.4 | ±0.006 | ±0.15 |
| 1½<OD<2 | 38.1< OD<50.8 | ±0.008 | ±0.2 |
| 2≤ OD<2½ | 50.8≤ OD<63.5 | ±0.010 | ±0.25 |
| 2½≤ OD<3 | 63.5≤ OD<76.2 | ±0.012 | ±0.30 |
| 3≤ OD ≤4 | 76.2≤ OD ≤101.6 | ±0.015 | ±0.38 |
| 4<OD ≤7½ | 101.6<OD ≤190.5 | -0.025 - +0.015 | -0.64 - +0.038 |
| 7½< OD ≤9 | 190.5< OD ≤228.6 | -0.045 - +0.015 | -1.14 - +0.038 |
After insertion into the boiler, the tube should be able to withstand expansion and bending without cracking defects or cracking at welds.
The superheater tubing shall be capable of withstanding all necessary forging, welding, and bending operations without defects.
Mainly used in boiler tubes, boiler flues, superheater flues, and safe ends.
ASTM A178 Grade A tubing's low carbon content gives it good weldability and high toughness for applications that are not subjected to high pressures.
It is primarily used for low-pressure and medium-temperature applications such as low-pressure boilers (e.g., domestic boilers, small office building,s or factory boilers) and other heat exchangers in low-temperature environments.
ASTM A178 Grade C has higher carbon and manganese content giving this tube better strength and heat resistance for more demanding operating conditions.
Suitable for medium pressure and medium temperature applications such as industrial and hot water boilers, which typically require higher pressures and temperatures than domestic boilers.
ASTM A178 Grade D tubes have a high manganese content and appropriate silicon content to provide excellent strength and heat resistance, making them stable in high-temperature and high-pressure environments and suitable for withstanding extreme operating conditions.
Typically used in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, such as power station boilers and industrial superheaters.
1. ASTM A179 / ASME SA179: Seamless mild steel heat exchanger and condenser tubes for cryogenic service. Primarily used in lower pressure environments, it is similar in chemical and mechanical properties to ASTM A178.
2. ASTM A192 / ASME SA192: Seamless carbon steel boiler tubes in high pressure service. Primarily used in the manufacture of water walls, economizers and other pressure components for ultra-high pressure boilers.
3. ASTM A210 / ASME SA210: Covers seamless medium carbon and alloy steel boiler and superheater tubes for high temperature and medium pressure boiler systems.
4. DIN 17175: Seamless steel tubes and pipes for use in high pressure and high temperature environments. Mainly used in the manufacture of steam pipes for boilers and pressure vessels.
5. EN 10216-2: Prescribes technical conditions for seamless tubes and pipes of non-alloy and alloy steels with specified high-temperature properties for applications under pressure.
6. JIS G3461: Covers carbon steel tubes for boilers and heat exchangers. It is suitable for general low and medium pressure heat exchange situations.
We are a high-quality welded carbon steel pipe manufacturer and supplier from China, and also a seamless steel pipe stockist, offering you a wide range of steel pipe solutions!
For any inquiries or to learn more about our offerings, don't hesitate to contact us. Your ideal steel pipe solutions are just a message away!












