ASTM A214 steel tubing is electric-resistance-welded carbon steel tubing for use in heat exchangers, condensers, and similar heat transfer equipment. It is typically applied to steel tubing with an outside diameter not greater than 3in [76.2mm].
Normally applicable steel pipe sizes are not larger than 3in [76.2mm].
Other sizes of ERW steel pipe may be furnished, provided such pipe meets all other requirements of this specification.
Material furnished under this specification shall conform to the applicable requirements of the current edition of Specification A450/A450M. unless otherwise provided herein.
Tubes shall be made by electric-resistance welding (ERW).
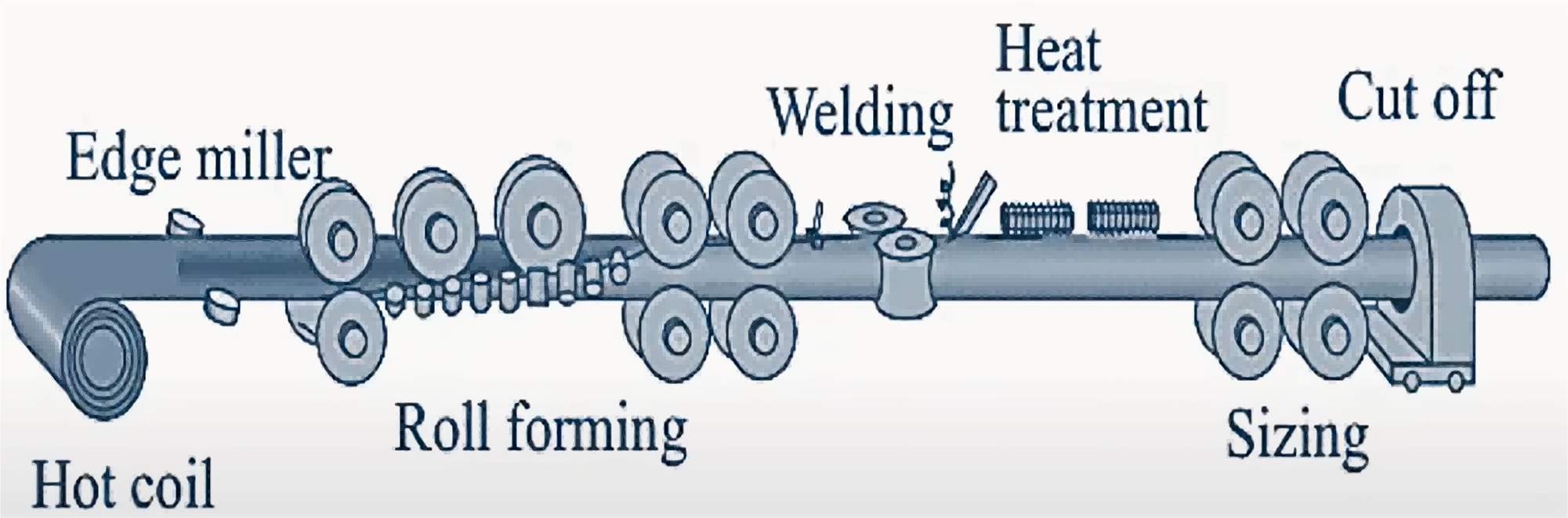
With its low manufacturing cost, high dimensional accuracy, excellent strength and durability, and design flexibility, ERW steel pipe has become the preferred material for a wide range of industrial piping systems, structural engineering, and a variety of infrastructure projects.
After welding, all tubes shall be heat treated at a temperature of 1650°F [900°] or higher and followed by cooling in air or in the cooling chamber of a controlled atmosphere furnace.
Cold-drawn tubes shall be heat treated after the final cold-draw pass at a temperature of 1200°F [650°C] or higher.
| C (Carbon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulfur) |
| max 0.18% | 0.27-0.63 | max 0.035% | max 0.035% |
It is not permissible to supply grades of alloy steel that specifically call for the addition of any element other than those listed.
Mechanical requirements do not apply to tubing with an inside diameter less than 0.126 in [3.2 mm] or a thickness less than 0.015 in [0.4 mm].
Tensile Property
There are no specific requirements for tensile properties in ASTM A214.
This is because ASTM A214 is primarily used for heat exchangers and condensers. The design and operation of these devices do not typically place high pressures on the tubing. In contrast, more attention is given to the tube's ability to withstand pressure, its heat transfer properties, and its corrosion resistance.
Flattening Test
For welded pipe, the required test section length is not less than 4 in (100 mm).
The experiment was conducted in two steps:
The first step is the ductility test, the inner or outer surface of the steel pipe, there shall be no cracks or breaks until the distance between the plates is less than the value of H calculated according to the following formula.
H=(1+e)t/(e+t/D)
H = distance between flattening plates, in. [mm],
t = specified wall thickness of the tube, in.[mm],
D = specified outside diameter of the tube, in. [mm],
e = 0.09(deformation per unit length)(0.09 for low-carbon steel (maximum specified carbon 0.18 % or less)).
The second step is the integrity test, which shall continue to be flattened until the specimen breaks or the pipe walls meet. Throughout the flattening test, if laminated or unsound material is found, or if the weld is incomplete, it shall be rejected.
Flange Test
A section of pipe must be capable of being flanged over to a position at right angles to the body of the pipe without cracking or imperfections that could be rejected under the provisions of the product specification.
The width of the flange for carbon and alloy steels shall be not less than the percentages.
| Outside Diameter | Width of Flange |
| To 2½in[63.5mm], incl | 15% of OD |
| Over 2½ to 3¾ [63.5 to 95.2], incl | 12.5% of OD |
| Over 3¾ to 8 [95.2 to 203.2], incl | 15% of OD |
Reverse Flattening Test
A 5 in. [100 mm] in length of finished welded tubing in sizes down to and including ½ in. [12.7 mm] in outside diameter shall be split longitudinally 90° on each side of the weld and the sample opened and flattened with the weld at the point of maximum bend.
There shall be no evidence of cracks lack of penetration or overlaps resulting from flash removal in the weld.
Hardness Test
The hardness of the tube shall not exceed 72 HRBW.
For tubes 0.200 in [5.1 mm] and over in wall thickness, either the Brinell or Rockwell hardness test shall be used.
Hydrostatic or non-destructive electrical testing is performed on each steel pipe.
Hydrostatic Test
The maximum pressure value should be maintained for at least 5s without leakage.
The minimum hydrostatic test pressure is related to the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe. It can be calculated by the formula.
Inch-Pound Units: P = 32000 t/D or SI Units: P = 220.6 t/D
P = hydrostatic test pressure, psi or MPa,
t = specified wall thickness, in. or mm,
D = specified outside diameter, in. or mm.
Maximum experimental pressure, to comply with the requirements below.
| Outside Diameter of Tube | Hydrostatic Test Pressure, psi [MPa] | |
| OD <1 in | OD <25.4 mm | 1000 [7] |
| 1≤ OD <1½ in | 25.4≤ OD <38.1 mm | 1500 [10] |
| 1½≤ OD <2 in | 38.≤ OD <50.8 mm | 2000 [14] |
| 2≤ OD <3 in | 50.8≤ OD <76.2 mm | 2500 [17] |
| 3≤ OD <5 in | 76.2≤ OD <127 mm | 3500 [24] |
| OD ≥5 in | OD ≥127 mm | 4500 [31] |
Nondestructive Electric Test
Each tube shall be examined by non-destructive testing methods in accordance with Specification E213, Specification E309 (ferromagnetic materials), Specification E426 (non-magnetic materials), or Specification E570.
The following data is derived from ASTM A450 and meets the relevant requirements for welded steel pipe only.
Weight Deviation
0 - +10%, no downward deviation.
The weight of a steel pipe can be calculated by the formula.
W = C(D-t)t
W= weight, Ib/ft [kg/m],
C= 10.69 for Inch Units [0.0246615 for SI Units],
D = specified outside diameter, in. [mm],
t = specified minimum wall thickness, in. [mm].
Wall Thickness Deviation
0 - +18%.
The variation in wall thickness of any one section of steel pipe 0.220 in [5.6 mm] and above shall not exceed ±5 % of the actual average wall thickness of that section.
The average wall thickness is the average of the thickest and thinnest wall thicknesses in the section.
Outside Diameter Deviation
| Outside Diameter | Permissible Variations | ||
| in | mm | in | mm |
| OD ≤1 | OD ≤ 25.4 | ±0.004 | ±0.1 |
| 1< OD ≤1½ | 25.4< OD ≤38.4 | ±0.006 | ±0.15 |
| 1½< OD <2 | 38.1< OD <50.8 | ±0.008 | ±0.2 |
| 2≤ OD <2½ | 50.8≤ OD <63.5 | ±0.010 | ±0.25 |
| 2½≤ OD <3 | 63.5≤ OD <76.2 | ±0.012 | ±0.30 |
| 3≤ OD ≤4 | 76.2≤ OD ≤101.6 | ±0.015 | ±0.38 |
| 4< OD ≤7½ | 101.6< OD ≤190.5 | -0.025 - +0.015 | -0.64 - +0.038 |
| 7½< OD ≤9 | 190.5< OD ≤228.6 | -0.045 - +0.015 | -1.14 - +0.038 |
The finished lubes shall be free of scale. A slight amount of oxidation shall not be considered as scale.
Each tube shall be clearly labeled with the manufacturer's name or brand, specification number, and ERW.
The manufacturer's name or symbol may be placed permanently on each tube by rolling or light stamping before normalizing.
If a single stamp is placed on the tube by hand, this mark should not be less than 8 in. [200 mm] from one end of the tube.
Resistance to high temperatures and pressures: The ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures is a very important property in heat exchange systems.
Good thermal conductivity: The materials and manufacturing process of this steel tube ensure excellent thermal conductivity for applications requiring efficient heat exchange.
Weldability: Another advantage is that they can be well connected by welding, making installation and maintenance easier.
Mainly used in heat exchangers, condensers, and similar heat transfer equipment.
1. Heat exchangers: In various industrial processes, heat exchangers are used to transfer heat energy from one fluid (liquid or gas) to another without allowing them to come into direct contact. ASTM A214 steel tubes are widely used in this type of equipment because they can withstand the high temperatures and pressures that can occur in the process.
2. Condensers: Condensers are mainly used for heat removal in cooling processes, e.g. in refrigeration and air-conditioning systems, or for converting steam back to water in power stations. They are used in these systems because of their good thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
3. Heat exchange equipment: This type of steel tube is also used in other heat exchange equipment similar to heat exchangers and condensers, such as evaporators and coolers.
ASTM A179: is a seamless cold-drawn mild steel heat exchanger and condenser tubing. It is typically used in applications with similar applications, such as heat exchangers and condensers. Although A179 is seamless, it provides similar heat exchange properties.
ASTM A178: Covers resistance-welded carbon and carbon-manganese steel boiler tubes. These tubes are used in boilers and superheaters, and can also be used in heat exchange applications with similar needs, especially where welded members are required.
ASTM A192: covers seamless carbon steel boiler tubes for high-pressure service. While these tubes are primarily intended for use in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, their materials and manufacturing processes make them suitable for use in other heat transfer equipment requiring high pressure and temperature resistance.
We are a high-quality welded carbon steel pipe manufacturer and supplier from China, and also a seamless steel pipe stockist, offering you a wide range of steel pipe solutions!
For any inquiries or to learn more about our offerings, don't hesitate to contact us. Your ideal steel pipe solutions are just a message away!















