ASTM A53 ERW steel pipe is Type E in the A53 specification, manufactured by the resistance welding process, and is available in both Grade A and Grade B grades.
It is primarily suited for mechanical and pressure applications and is also often used as a general purpose for conveying steam, water, gas, and air.
The advantages of ERW steel pipe, such as low price and high productivity, make it the material of choice for many industrial applications.
Botop Steel is a high-quality welded carbon steel pipe manufacturer and supplier from China, and also a seamless steel pipe stockist, offering you a wide range of steel pipe solutions!
Our inventory is well stocked and we are able to meet our customers' rapid demand for a wide range of sizes and quantities.
ASTM A53/A53M includes the following types and grades:
Type E: Electric-resistance-welded, Grades A and B.
Type S: Seamless, Grades A and B.
Type F: Furnace-butt-welded, continuous welded Grades A and B.
Type E and Type S are two widely used pipe types. In contrast, Type F is typically used for smaller diameter tubes. Due to advances in welding technology, this manufacturing method is used less frequently.
Nominal Diameters: DN 6 - 650 [NPS 1/8 - 26];
Outer Diameter: 10.3 - 660 mm [0.405 - 26 in.];
Wall thickness and steel pipe weight charts:
ASTM A53 also permits the furnishing of pipe with other dimensions provided the pipe meets all other requirements of this specification.
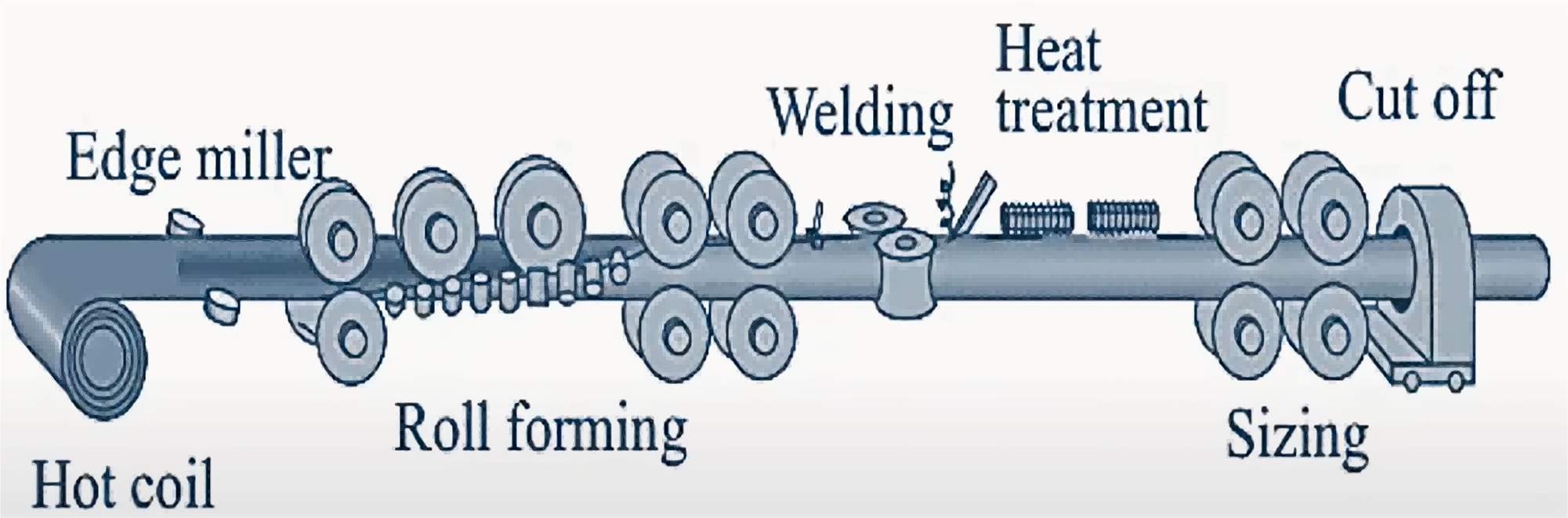
ERW is widely used to manufacture round, square, and rectangular carbon and low alloy steel pipes.
The following make is the production process for producing round ERW steel pipe:
a) Material preparation: The initial material is usually hot-rolled steel coils. These coils are first flattened and sheared to the required width.
b) Forming: Gradually, through a series of rolls, the strip is formed into an open circular tubular structure. During this process, the edges of the strip are gradually brought closer together in preparation for welding.
c) Welding: After forming the tubular structure, the edges of the steel strip are heated by electrical resistance in the welding zone. A high-frequency current is passed through the material, and the heat generated by the resistance is used to heat the edges to their melting point, and then they are welded together by pressure.
d) Deburring: After welding, weld burrs (excess metal from welding) are removed from the inside and outside of the pipe to ensure a smooth surface inside the pipe.
e) Sizing and length setting: After welding and deburring are completed, the tubes are passed through a sizing machine for dimensional correction to ensure that they meet the exact diameter and roundness requirements. The tubes are then cut to predetermined lengths.
f) Inspection and testing: The steel pipe will undergo strict testing and inspection, including ultrasonic testing, hydrostatic testing, etc., to ensure that the quality of the steel pipe meets the standards and specifications.
g) Surface treatment: Finally, the steel pipe may be subjected to further treatments such as hot dip galvanizing, painting, or other surface treatments to provide additional corrosion protection and aesthetics.
Welds in Type E or Type F Grade B pipe shall be heat-treated or otherwise treated after welding so that untempered martensite is not present.
The heat treatment temperature shall be at least 1000°F [540°C].
When pipe is cold expanded, the expansion shall not exceed 1.5% of the specified outside diameter of the pipe.
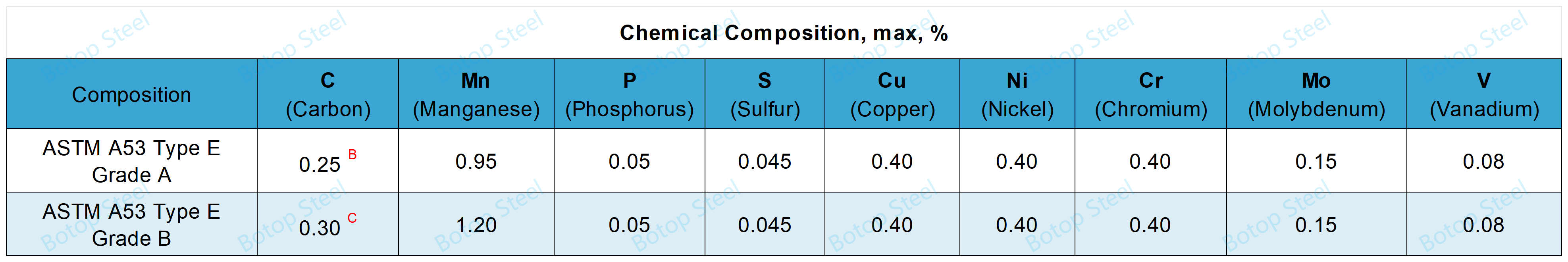
A The five elements Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo, and V together must not exceed 1.00%.
B For each reduction of 0.01 % below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06 % of manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.35 %.
C For each reduction of 0.01 % below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06 % of manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.65 %.
Tensile Property
| List | Classification | Grade A | Grade B |
| Tensile strength, min | MPa [psi] | 330 [48,000] | 415 [60,000] |
| Yield strength, min | MPa [psi] | 205 [30,000] | 240 [35,000] |
| Elongation in 50 mm [2 in.] | Note | A, B | A, B |
Note A: The minimum elongation in 2 in[50 mm] shall be that determined by the following equation:
e = 625,000 [1940] A0.2/U0.9
e = minimum elongation in 2 in or 50 mm in percent, rounded to the nearest percent
A = the lesser of 0.75 in2 [500 mm2] and the cross-sectional area of the tension test specimen, calculated using the specified outside diameter of the pipe, or the nominal width of the tension test specimen and the specified wall thickness of the pipe, with the calculated value rounded to the nearest 0.01 in2 [1 mm2].
U=specified minimum tensile strength, psi [MPa].
Note B: See Table X4.1 or Table X4.2, whichever is applicable, for the minimum elongation values that are required for various combinations of tension test specimen size and specified minimum tensile strength.
Bend Test
For pipe DN ≤ 50 [NPS ≤ 2], a sufficient length of pipe shall be capable of being bent cold through 90° around a cylindrical mandrel, the diameter of which is twelve times the specified outside diameter of the pipe, without developing cracks at any portion and without opening the weld.
Double-extra-strong (weight class: XXS) pipe over DN 32 [NPS 1 1/4] need not be subjected to the bend test.
Flattening Test
The flattening test shall be made on welded pipe over DN 50 in extra-strong weight (XS) or lighter.
Suitable for Type E, Grade A and B; and Type F, Grade B tubes.
Seamless steel tubes do not have to be tested.
Test Time
For all sizes of Type S, Type E, and Type F Grade B piping, the experimental pressure shall be maintained for a minimum of 5s.
The hydrostatic test shall be applied, without leakage through the weld seam or the pipe body.
Test Pressures
Plain-end pipe shall be hydrostatically tested to the applicable pressure given in Table X2.2,
Threaded-and-coupled pipe shall be hydrostatically tested to the applicable pressure given in Table X2.3.
For steel pipes with DN ≤ 80 [NPS ≤ 80], the test pressure shall not exceed 17.2MPa;
For steel pipes with DN >80 [NPS >80], the test pressure shall not exceed 19.3MPa;
Higher experimental pressures can be selected if there are special engineering requirements, but this requires negotiation between the manufacturer and the customer.
Marking
If the pipe was hydrostatically tested, the marking should indicate the test pressure.
The following requirements apply to Type E and Type F Grade B Pipe.
Seamless pipe has additional requirements that are not discussed in this document.
Test Methods
Pipes produced by non-hot-stretch expansion and contraction machines: DN ≥ 50 [NPS ≥ 2], the welds in each section of the pipe need to pass a non-destructive electrical test, and the test method needs to be in accordance with the E213, E273, E309 or E570 standard.
ERW pipes produced by hot- stretch-reducing diameter machine: DN ≥ 50 [NPS ≥ 2] Each section of pipe shall be fully inspected in its entirety by non-destructive electrical testing, which shall be in accordance with the E213, E309, or E570 standards.
Note: Hot Stretch Expansion Diameter Machine is a machine that continuously stretches and squeezes steel tubes by rollers at high temperatures to adjust their diameters and wall thicknesses.
Marking
If the tube has been subjected to non-destructive examination, it is necessary to indicate NDE on the marking.
Mass
±10%.
Pipe DN ≤ 100 [NPS ≤ 4], weighed as a batch.
Pipes DN > 100 [NPS > 4], weighed in single pieces.
Diameter
For pipe DN ≤40 [NPS≤ 1 1/2], OD variation shall not exceed ±0.4 mm [1/64 in.].
For pipe DN ≥50 [NPS>2], OD variation shall not exceed ±1%.
Thicknesses
The minimum wall thickness shall not be less than 87.5% of the specified wall thickness.
lighter than extra-strong (XS) weight:
a) plain-end pipe: 3.66 - 4.88m [12 - 16 ft], Not more than 5% of the total number.
b) double-random lengths: ≥ 6.71 m [22 ft], Minimum average length of 10.67m [35 ft].
c) single-random lengths: 4.88 -6.71m [16 - 22 ft], not more than 5 % of the total number of threaded lengths furnished being jointers (two pieces coupled together).
Extra-strong (XS) weight or heavier: 3.66-6.71 m [12 - 22 ft], no more than 5% total of pipe 1.83 - 3.66 m [6 - 12 ft].
For ASTM A53 steel pipe finish is available in black or galvanized.
Black: Steel tubing without any surface treatment, usually sold directly after the manufacturing process, for those applications where no additional corrosion resistance is required.
Galvanized pipes should meet the relevant requirements.
Process
The zinc shall be coated internally and externally by the hot-dip process.
Raw Material
The zinc used for the coating shall be any grade of zinc conforming to the requirements of Specification ASTM B6.
Appearance
Galvanized pipe shall be free of uncoated areas, air bubbles, flux deposits, and coarse slag inclusions. Lumps, bumps, globules, or large amounts of zinc deposits that interfere with the intended use of the material shall not be permitted.
Galvanized Coating Weight
Shall be determined by peel test according to test method ASTM A90.
Coating weight should not be less than 0.55 kg/m² [ 1.8 oz/ft² ].
ASTM A53 ERW steel pipe is typically used in low to medium-pressure applications such as municipal engineering, construction, and mechanical structural pipe. Common use scenarios include conveying water, steam, air, and other low-pressure liquids.
With good weldability, they are suitable for forming operations involving coiling, bending, and flanging.





















