ASTM A513 steel is a carbon and alloy steel pipe and tube made from hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel as raw material by electric resistance welding (ERW) process, which is widely used in all kinds of mechanical structures.

Navigation Buttons
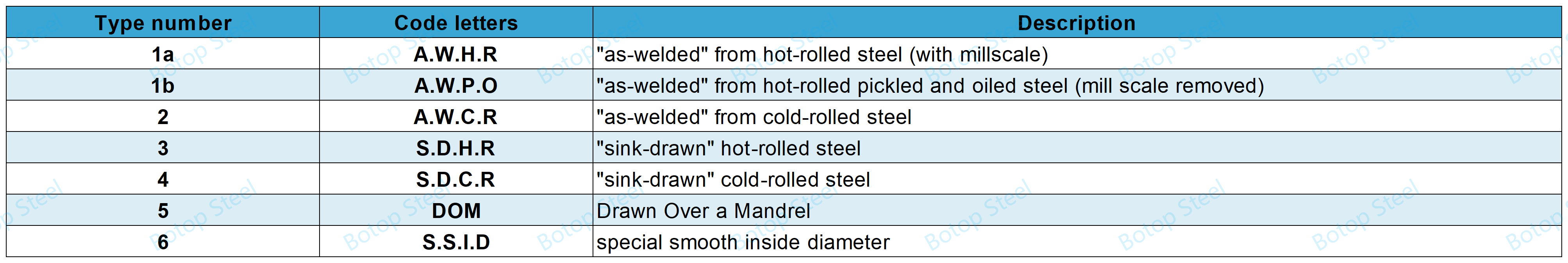
Types and Thermal Conditions of ASTM A513
Grade Classification
ASTM A513 Size Range
Hollow Section Shape
Raw Materials
ASTM A513 Manufacturing Processes
Hot Treatment
Welding Seam Handling
Chemical Composition of ASTM A513
Mechanical Properties of ASTM A513
Hardness Test
Flattening Test
Flaring Test
Hydrostatic Test Round Tubing
Nondestructive Electric Test
Tolerances for Round Pipe Dimensions
Tolerance of Square and Rectangular Tube Dimensions
Appearances
Coating
Marking
ASTM A513 Applications
Our Advantages
Types and Thermal Conditions of ASTM A513
The division is based on the different conditions or processes of the steel pipe.
Grade Classification
ASTM A513 can be either carbon or alloy steel, depending on the actual application.
Carbon Steel
MT 1010, MT 1015, MT X 1015, MT 1020, MT X 1020.
1006, 1008, 1009, 1010, 1012, 1015, 1016, 1017, 1018, 1019, 1020, 1021, 1022, 1023, 1024, 1025, 1026, 1027, 1030, 1033, 1035, 1040, 1050, 1060, 1524.
Alloys Steel
1340, 4118, 4130, 4140, 5130, 8620, 8630.
ASTM A513 Size Range

Hollow Section Shape
Round
Square or rectangular
Other shapes
such as streamlined, hexagonal, octagonal, round inside and hexagonal or octagonal outside, ribbed inside or out, triangular, rounded rectangular and D shapes.
Raw Materials
The steel may be made by any process.
The primary melting may incorporate separate degassing or refining and may be followed by secondary melting, such as electro slag or vacuum-arc remelting.
Steel may be cast in ingots or may be strand cast.
ASTM A513 Manufacturing Processes
Tubes shall be made by the electric-resistance-welded (ERW) process and shall be made from hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel as specified.
ERW pipe is the process of creating a weld by coiling a metallic material into a cylinder and applying resistance and pressure along its length.
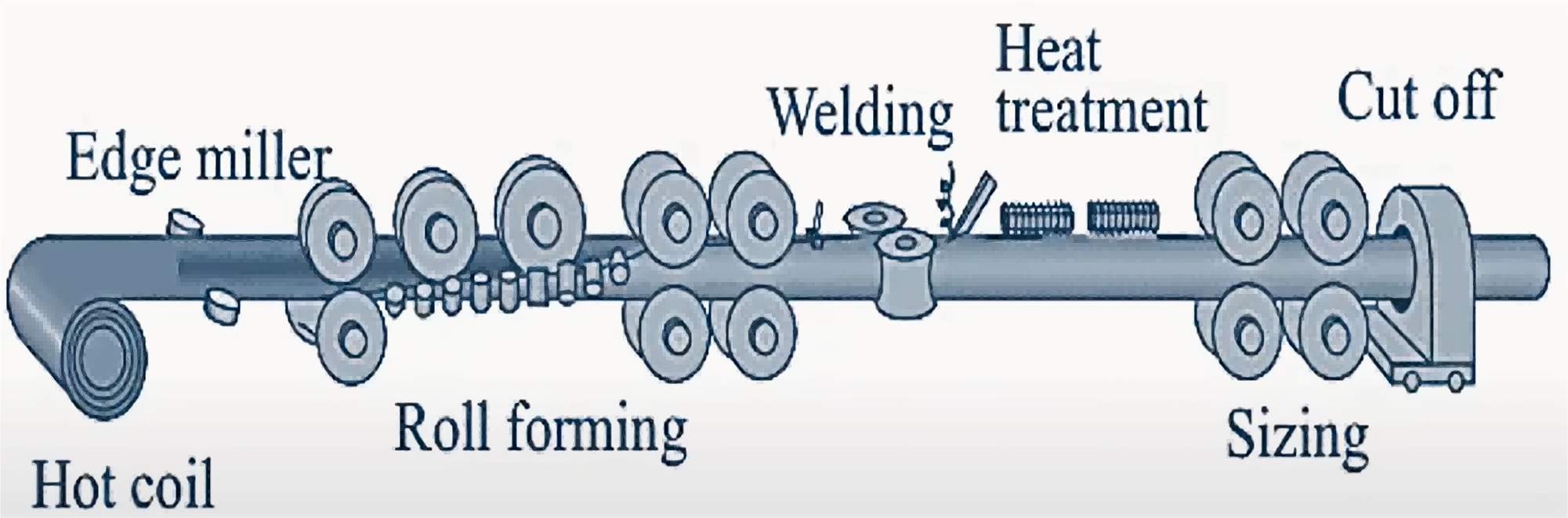
Hot-Rolled Steel: In the production process, hot-rolled steel is first heated at high temperatures, allowing the steel to be rolled in a plastic state, which makes it easy to change the shape and size of the steel. At the end of the hot rolling process, the material is usually scaled and deformed.
Cold-Rolled Steel: Cold-rolled steel is rolled further after the material has cooled to achieve the desired size and shape. This process is usually done at room temperature and results in steel with better surface quality and more accurate dimensions.
Hot Treatment

When the thermal condition is not specified, the tube may be supplied in the NA condition.
When a final thermal treatment is specified, a tight oxide is normal.
When an oxide-free surface is specified, the tube may be bright annealed or pickled at the manufacturer's option.
Welding Seam Handling
External welds must be cleaned
Internal welds will have different height requirements depending on the Type.
Specific requirements can be found in ASTM A513, section 12.3.
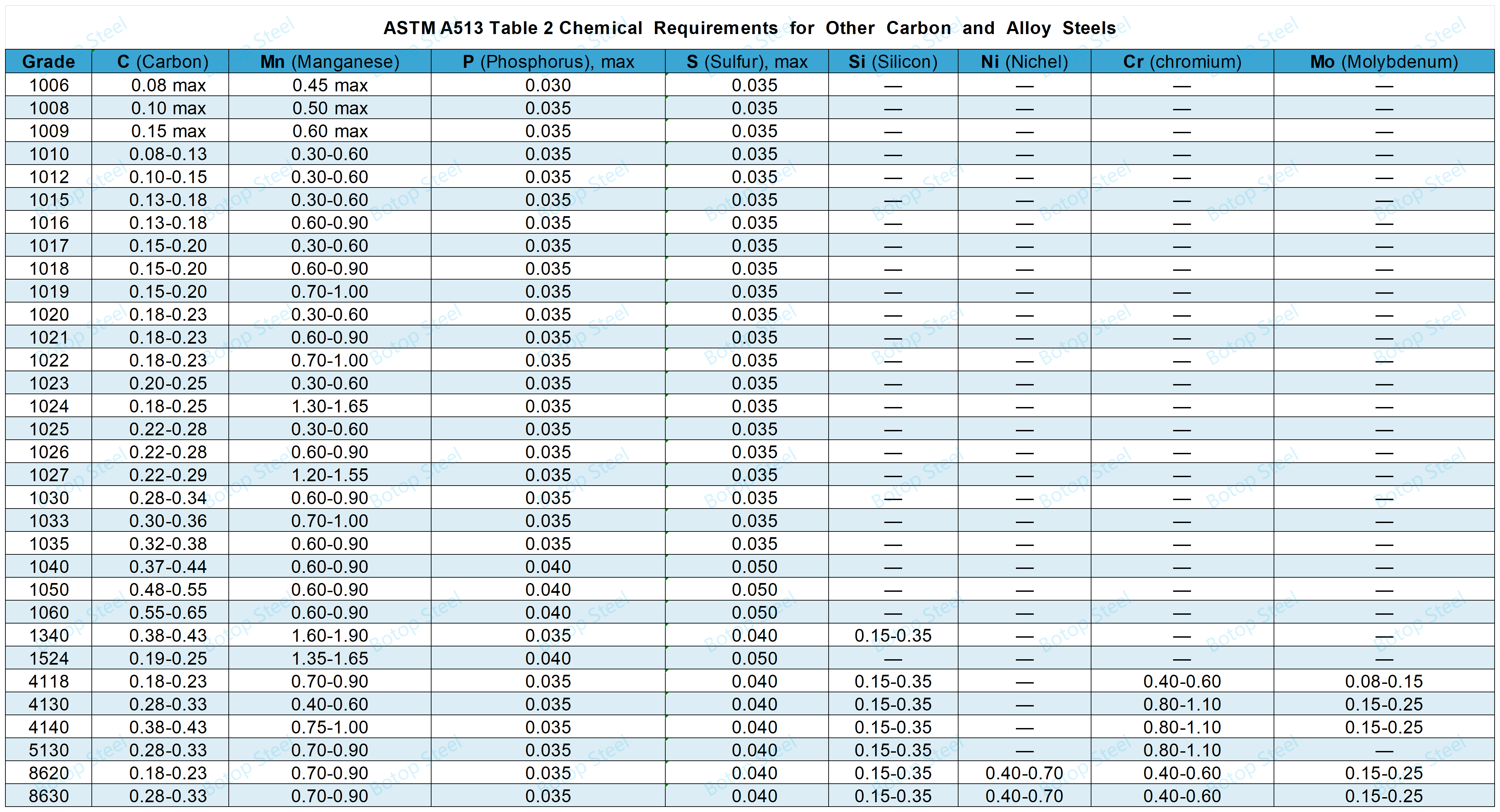
Chemical Composition of ASTM A513
Steel shall conform to the chemical composition requirements specified in Table 1 or Table 2.
When carbon steel grades are ordered from a standard, it is not permissible to provide alloy grades that specifically call for the addition of any element other than those listed in Tables I and 2.
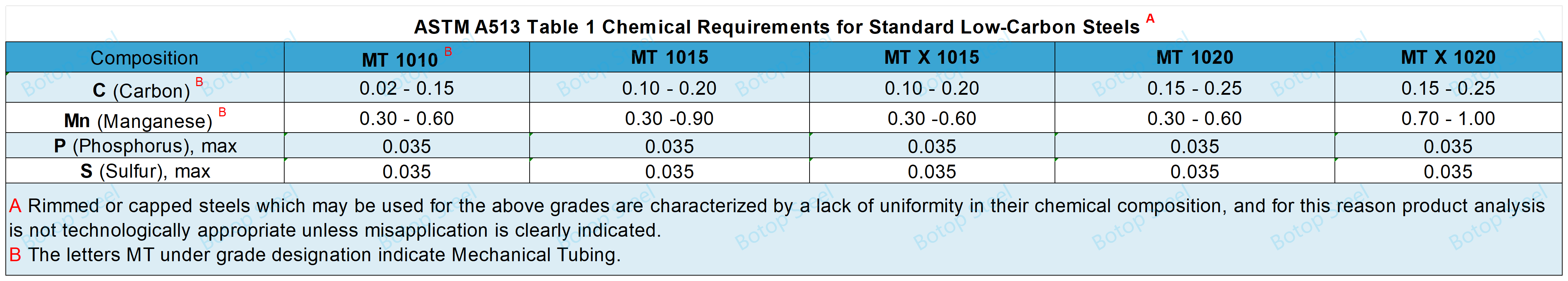
If no grade is specified, grades MT 1010 through MT 1020 are available.
Mechanical Properties of ASTM A513
Tensile testing shall be performed once per lot.
When "Required Tensile Properties" are specified in the Purchase Order, round tubing shall conform to the tensile requirements and not necessarily to the hardness limits shown in Table 5.
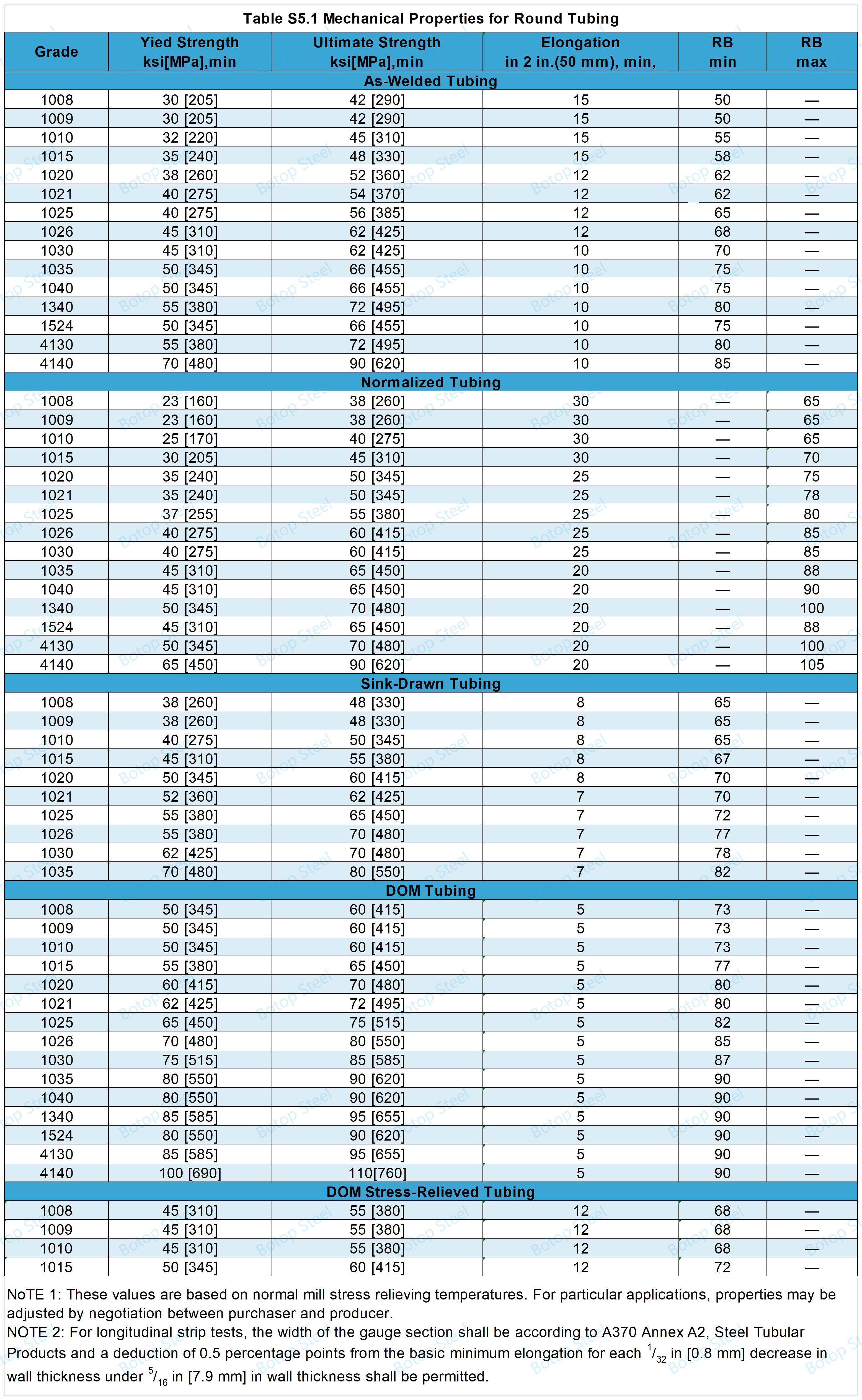
Hardness Test
1% of all tubes in each lot and not less than 5 tubes.
Flattening Test
Round tubes and tubes that form other shapes when they are round are applicable.
No opening in the weld shall take place until the distance between the plates is less than two-thirds of the original outside diameter of the tubing.
No cracks or breaks in the base metal shall occur until the distance between the plates is less than one-third of the original outside diameter of the tubing but in no case less than five times the thickness of the tubing wall.
Evidence of lamination or burnt material shall not develop during the flattening process, and the weld shall not show injurious defects.
Note: When low D-to-t ratio tubing is tested, because the strain imposed due to geometry is unreasonably high on the inside surface at the six and twelve o'clock locations, cracks at these locations shall not be cause for rejection if the D-to-t ratio is less than 10.
Flaring Test
Round tubes and tubes that form other shapes when they are round are applicable.
A section of tube approximately 4 in.[100 mm] in length shall stand being flared with a tool having a 60° included angle until the tube at the mouth of the flare has been expanded 15 % of the inside diameter, without cracking or showing flaws.
Hydrostatic Test Round Tubing
All tubing will be given a hydrostatic test.
Maintain the minimum hydro test pressure for not less than 5s.
The pressure is calculated as:
P=2St/D
P = minimum hydrostatic test pressure, psi or MPa,
S = allowable fiber stress of 14,000 psi or 96.5 MPa,
t = specified wall thickness, in. or mm,
D = specified outside diameter, in. or mm.
Nondestructive Electric Test
It is the intent of this test to reject tubes containing injurious defects.
Each tube shall be tested with a nondestructive electric test in accordance with Practice E213, Practice E273, Practice E309, or Practice E570.
Tolerances for Round Pipe Dimensions
For more information, please see the corresponding table in the standard.
Outer Diameter
Table 4 Diameter Tolerances for Type I (A.W.H.R.) Round Tubing
Table 5 Diameter Tolerances for Types 3, 4, 5, and 6 (S.D.H.R., S.D.C.R., DOM, and S.S.I.D.) Round Tubing
Table 10 Diameter Tolerances for Type 2 (A.W.C.R.) Round Tubing
Wall Thickness
Table 6 Wall Thickness Tolerance for Type I (A.W.H.R.) Round Tubing (Inch Units)
Table 7 Wall Thickness Tolerance for Type I (A.W.H.R.) Round Tubing (SI Units)
Table 8 Wall Thickness Tolerances of Types 5 and 6 (DOM and S.S.I.D.) Round Tubing (Inch Units)
TABLE 9 Wall Thickness Tolerances of Types 5 and 6 (DOM and S.S.I.D.) Round Tubing (SI Units)
Table 11 Wall Thickness Tolerances for Type 2 (A.W.C.R.) Round Tubing (Inch Units)
Table 12 Wall Thickness Tolerances for Type 2 (A.W.C.R.) Round Tubing (SI Units)
Length
Table 13 Cut-Length Tolerances for Lathe-Cut Round Tubing
Table 14 Length Tolerances for Punch-, Saw-, or Disc-Cut Round Tubing
Squareness
Table 15 Tolerance (Inch) for Squareness of Cut (Either End) When Specified for Round Tubing
Tolerance of Square and Rectangular Tube Dimensions
For more information, please see the corresponding table in the standard.
Outer Diameter
Table 16 Tolerances, Outside Dimensions Square and Rectangular Tubing
Radii of Corners
Table 17 Radii of Corners of Electric-Resistance-Welded Square and Rectangular Tubing
Length
Table 18 Length Tolerances-Square and Rectangular Tubing
Twist Tolerances
Table 19 Twist Tolerances Electric-Resistance-Welded for Square and Rectangular-Mechanical Tubing
Appearances
The tubing shall be free of injurious defects and shall have a workmanlike finish.
Coating
Tubing shall be coated with a film of oil before shipping to retard rust.
Prevents rust from occurring in a short period of time.
Should the order specify that tubing be shipped without rust retarding oil, the film of oils incidental to manufacture will remain on the surface.
Marking
The surface of the steel is marked using a suitable method and contains the following information:
Manufacturer name or brand
Specified size
Type
purchaser's order number,
Standard number, ASTM A513.
Barcodes can also be used as a complementary identification method.
ASTM A513 Applications
Automotive industry: Used in automotive seat frames, suspension components, steering columns, brackets, and other vehicle structural components.
Construction industry: as a support material for building structures, such as scaffolding tubes, guardrails, railings, etc.
Machinery manufacturing: Used in the production of various mechanical components, such as hydraulic system cylinders, rotating parts, bearings, and so on.
Agricultural equipment: In agricultural machinery manufacturing, used to make structural parts of farming equipment, transmission systems, etc.
Furniture Manufacturing: Used in the production of various metal furniture, such as bookshelves, chair frames, bed frames, and so on.
Sports equipment: in the sports facilities and equipment manufacturing, used as metal parts, such as fitness equipment, basketball goals, soccer goals, etc.
Industrial facilities: used in the manufacture of conveyor belts, rollers, tanks, and other industrial equipment components.
Our Advantages
Since its establishment in 2014, Botop Steel has become a leading carbon steel pipe supplier in Northern China, known for its excellent service, high-quality products, and comprehensive solutions. The company's extensive product range includes seamless, ERW, LSAW, and SSAW steel pipes, as well as pipe fittings, flanges, and specialty steels.
With a strong commitment to quality, Botop Steel implements stringent controls and tests to ensure the reliability of its products. Its experienced team provides personalized solutions and expert support, with a focus on customer satisfaction.
Tags: ASTM A513, carbon steel, type 5, type 1, dom.
Post time: May-07-2024
