ASTM A671 is a steel pipe made from a pressure vessel quality plate, Electric-Fusion-Welded (EFW) for high-pressure environments at ambient and lower temperatures.
It is particularly suitable for applications requiring high-pressure stability and specific low-temperature properties.

Navigation Buttons
ASTM A671 Size Range
Recommended range: steel pipes with DN ≥ 400 mm [16 in] and WT ≥ 6 mm [1/4].
It may also be used for other sizes of pipe, provided it meets all other requirements of this specification.
ASTM A671 Marking
In order to better understand ASTM A671, let's first understand its marking content. This helps to clarify the scope of the application and characteristics of this standard.
Example of Spray Marking:
BOTOP EFW ASTM A671 CC60 -22 16"×SCH80 HEAT NO.4589716
BOTOP: Name of the manufacturer.
EFW: Steel tube manufacturing process.
ASTM A671: Executive Standard for Steel Tubing.
CC60-22: Abbreviations for grade:cc60 and class 22.
16" x SCH80: Diameter and Wall Thickness.
HEAT NO. 4589716: Heat no. for the production of steel tubes.
This is the common format of ASTM A671 spray labeling.
It is not difficult to find ASTM A671 in the grade and class two classifications, then these two classifications represent what is the meaning.
Grade Classification
Classified according to the type of plate used to manufacture steel tubes.
Different grades represent different chemical compositions and mechanical properties for different pressure and temperature conditions.
For example, some grades are plain carbon steels, while others are steels with added alloying elements, such as nickel steels.
| Pipe Grade | Type of Steel | ASTM Specification | |
| No. | Grade/class/type | ||
| CA 55 | plain carbon | A285/A285M | Gr C |
| CB 60 | plain carbon, killed | A515/A515M | Gr 60 |
| CB 65 | plain carbon, killed | A515/A515M | Gr 65 |
| CB 70 | plain carbon, killed | A515/A515M | Gr 70 |
| CC 60 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516/A516M | Gr 60 |
| CC 65 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516/A516M | Gr 65 |
| CC 70 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516/A516M | Gr 70 |
| CD 70 | manganese-silicon, normalized | A537/A537M | Cl 1 |
| CD 80 | manganese-silicon, quenched and tempered | A537/A537M | Cl 2 |
| CFA 65 | nickel steel | A203/A203M | Gr A |
| CFB 70 | nickel steel | A203/A203M | Gr B |
| CFD 65 | nickel steel | A203/A203M | Gr D |
| CFE 70 | nickel steel | A203/A203M | Gr E |
| CG 100 | 9% nickel | A353/A353M | |
| CH 115 | 9% nickel | A553/A553M | Type 1 |
| CJA 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr A |
| CJB 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr B |
| CJE 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr E |
| CJF 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr F |
| CJH 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr H |
| CJP 115 | alloy steel, quenched and tempered | A517/A517M | Gr P |
| CK 75 | carbon-manganese-silicon | A299/A299M | Gr A |
| CP 85 | alloy steel, age hardening, quenched and precipitation heat treated | A736/A736M | Gr A, Class 3 |
Class Classification
Tubes are categorized according to the type of heat treatment they receive during the manufacturing process and whether or not they are radiographically inspected and pressure tested.
The different categories reflect the different heat treatment specifications for tubes.
Examples include normalizing, stress relief, quenching, and tempered.
| Class | Heat treatment on pipe | Radiography, see note: |
Pressure test, see note: |
| 10 | none | none | none |
| 11 | none | 9 | none |
| 12 | none | 9 | 8.3 |
| 13 | none | none | 8.3 |
| 20 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | none | none |
| 21 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | 9 | none |
| 22 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 23 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | none | 8.3 |
| 30 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | none | none |
| 31 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | 9 | none |
| 32 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 33 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | none | 8.3 |
| 40 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | none | none |
| 41 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | 9 | none |
| 42 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 43 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | none | 8.3 |
| 50 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | none | none |
| 51 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | 9 | none |
| 52 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 53 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | none | 8.3 |
| 70 | quenched and precipitation heat treated | none | none |
| 71 | quenched and precipitation heat treated | 9 | none |
| 72 | quenched and precipitation heat treated | 9 | 8.3 |
| 73 | quenched and precipitation heat treated | none | 8.3 |
The temperature of use should be noted when selecting materials. Reference can be made to the specification ASTM A20/A20M.
Raw Materials
High quality plates for pressure vessels, details of types, and execution standards can be found in the table in Grade Classification above.
Welding Key Points
Welding: Seams shall be double-welded, full-penetration welded.
Welding shall be performed in accordance with procedures specified in Section IX of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
The welds shall be made either manually or automatically by an electric process involving the deposition of filler metal.
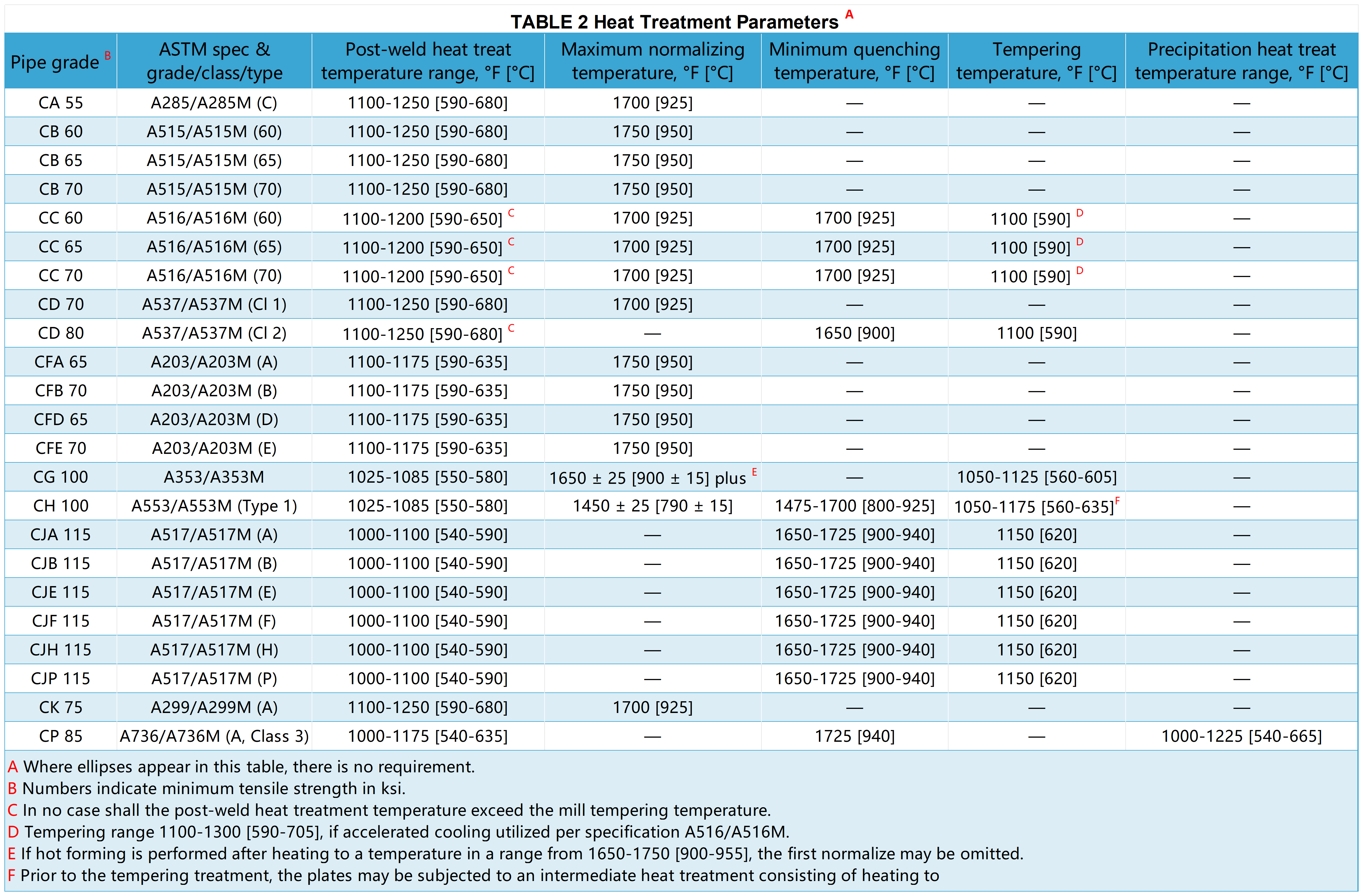
Heat Treatment for Different Classes
All classes other than 10, 11, 12, and 13 shall be heat treated in a furnace controlled to ±25 °F[± 15°C].
Classes 20, 21, 22, and 23
Shall be uniformly heated within the post-weld heat-treatment temperature range indicated in Table 2 for a minimum of 1 h/in. [0.4 h/cm] of thickness or for 1 h, whichever is greater.
Classes 30, 31, 32, and 33
Shall be uniformly heated to a temperature in the austenitizing range and not exceeding the maximum normalizing temperature indicated in Table 2 and subsequently cooled in the air at room temperature.
Classes 40, 41, 42, and 43
The pipe shall be normalized.
The pipe shall be reheated to the tempering temperature indicated in Table 2 as a minimum and held at a temperature for a minimum of 0.5 h/in.[0.2 h/cm] of thickness or for 0.5 h, whichever is greater, and air-cooled.
Classes 50, 51, 52, and 53
The pipe shall be uniformly heated to temperatures within the austenitizing range and not exceeding the maximum quenching temperatures shown in Table 2.
Subsequently, quench in water or oil. After quenching, the pipe shall be reheated to the minimum tempering temperature shown in Table 2 and held at that.
temperature for a minimum of 0.5 h/inch [0.2 h/cm] of thickness or 0.5 h, whichever is greater, and air-cooled.
Classes 70, 71, 72, and 73
The pipes shall be uniformly heated to a temperature in the austenitizing range, not exceeding the maximum quenching temperature indicated in Table 2,and subsequently quenched in water or oil.
After quenching the pipe shall be reheated into the precipitation heat treating range indicated in Table 2 for a time to be determined by the manufacturer.
ASTM A671 Experimental Projects
Chemical Composition
According to the corresponding requirements of the implementation standards of raw materials, chemical composition analysis, the results of the experiment to meet the standard requirements.
Tension Test
All welded pipes manufactured to this specification must have a cross-weld tensile test after final heat treatment, and the results must match the base material requirements for the ultimate tensile strength of the specified plate material.
Additionally, Grades CD XX and CJ XXX, when these are of Class 3x, 4x, or 5x, and Grade CP of 6x and 7x shall have a transverse base metal tensile test performed on specimens cut from finished pipe. The results of these tests shall meet the minimum mechanical test requirements of the plate specification.
Transverse Guided Weld Bend Test
The bend test shall be acceptable if no cracks or other defects exceeding 1/8 in. [3 mm] in any direction are present in the weld metal or between the weld and the base metal after bending.
Cracks that originate along the edges of the specimen during testing, and that are less than 1/4 in. [6 mm]measured in any direction shall not be considered.
Pressure Test
Classes X2 and X3 pipe shall be tested in accordance with Specification A530/A530M, Hydrostatic Test Requirements.
Radiographic Examination
The full length of each weld of Classes X1 and X2 shall be radiographically examined in accordance with and meet the requirements of ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII, Paragraph UW-51.
The radiographic examination may be performed prior to heat treatment.
ASTM A671 Appearance
The finished pipe shall be free of injurious defects and shall have a workmanlike finish.
Allowable Deviation in Size
| Sports | Tolerance Value | Note |
| Outside Diameter | ±0.5% | Based on the circumferential measurement |
| Out-of-Roundness | 1%. | Difference between major and minor outside diameters |
| Alignment | 1/8 in [3 mm] | Using a 10 ft [3 m] straight edge placed so that both ends are in contact with the pipe |
| Thickness | 0.01 in [0.3 mm] | Minimum wall thickness less than the specified nominal thickness |
| Lengths | 0 - +0.5in [0 - +13mm] |
unmachined ends |
Applications for ASTM A671 Steel Tubing
Energy Industry
Used to transport cryogenic fluids in natural gas treatment plants, refineries, and chemical processing facilities.
Industrial Refrigeration Systems
For use in the cryogenic portion of refrigeration and air conditioning systems to ensure system stability and safety.
Utilities
For storage and transportation facilities for liquefied gases.
Building and Construction
Applied to infrastructure projects at low temperatures or extreme environmental conditions, such as cold storage construction.
We are one of the leading welded carbon steel pipe and seamless steel pipe manufacturers and suppliers from China, with a wide range of high-quality steel pipe in stock, we are committed to providing you with a full range of steel pipe solutions. For more product details, please feel free to contact us, we look forward to helping you find the best steel pipe options for your needs!
Tags: ASTM a671, efw, cc 60, class 22, suppliers, manufacturers, factories, stockists, companies, wholesale, buy, price, quotation, bulk, for sale, cost.
Post time: Apr-19-2024
