Carbon steel pipe is a pipe made of carbon steel with a chemical composition that, when thermally analyzed, does not exceed a maximum limit of 2.00% for carbon and 1.65% for manganese.
Carbon steel pipe is a common piping material that is widely used in industry to transport liquids and gases.

Navigation Buttons
Classification of Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Size Range
Common Executive Standards for Carbon Steel Pipe
Key Parameters of Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon Steel Pipe Surface Coating
Advantages of Carbon Steel Pipe
Disadvantages of Carbon Steel Pipe
Application of Carbon Steel Pipe
How to Choose a Reliable Carbon Steel Pipe Supplier
About Us
Classification of Carbon Steel Pipe
Classification by Purpose
Structural pipes: mainly used in building structures, such as building supports, bridges, and industrial structures.
Transportation pipes: These carbon steel pipes are used to transport fluids such as oil, gas, and water.
Mechanical Tubes: Used in machinery and automation where precise dimensions and specific mechanical properties are required.
Boiler Tubes: Specialized for high-temperature and high-pressure environments, such as boilers in power stations and oil refineries.
Oil and gas well tubing: used in oil and gas extraction, which must be able to withstand extreme pressure and chemical corrosion.
Classification According to Manufacturing Process
Seamless steel pipe: steel pipe made by hot finish or cold finish process, no welded seam, commonly used in the occasion of high pressure.
Welded steel pipe: made from steel plate or strip coil into a tube, through the welding method of processing molding.
Welded steel pipe can be categorized according to the welding process:
Resistance Welded Steel Pipe (ERW): Welded roll-formed pipe by high-frequency resistance heating, production of carbon steel pipe with a smaller diameter and faster production speed.
Submerged Arc Welded Pipe (SAW): uses an automatic submerged arc welding process to produce carbon steel pipes with larger diameters or thicker wall thicknesses.
SAW steel pipe can also be divided into LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding) and SSAW (Spiral Submerged Arc Welded) according to the direction of the weld seam.
If you want to know the difference between SMLS,ERW,LSAW,SSAW, you can click to check it out.
Carbon Steel Pipe Size Range
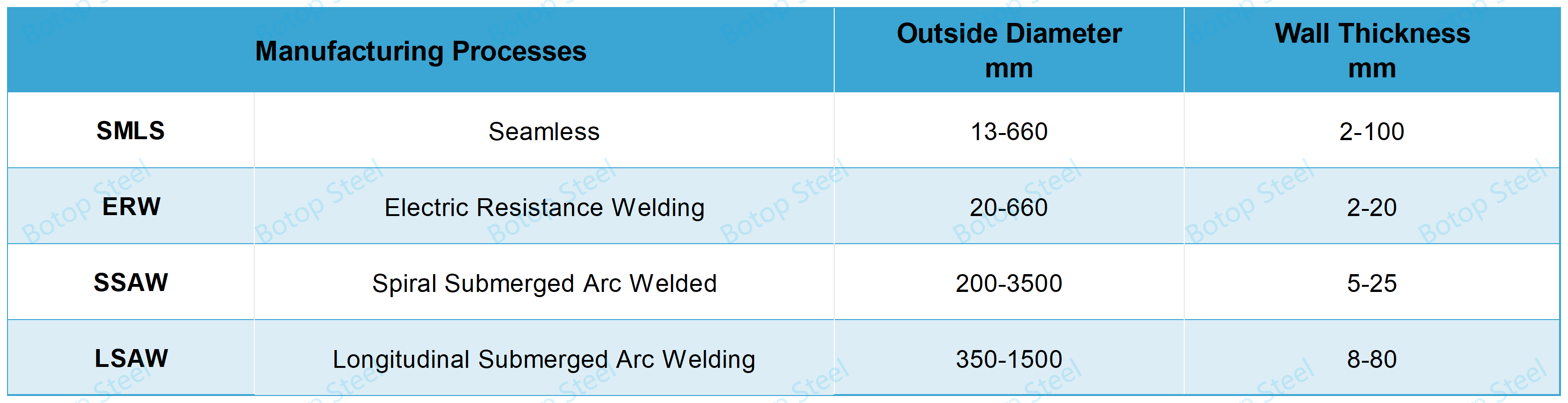
Common Executive Standards for Carbon Steel Pipe
ASTM A106: Seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service.
ASTM A53: Welded and seamless steel tubes for general and pressure service.
ASTM A333: Seamless and welded steel pipe for low-temperature service.
API 5L: Steel pipe specification for pipeline transportation systems used in the oil and gas industry.
DIN 2440: Medium-heavy carbon steel tubes for general structural and working pressure purposes.
EN 10210: Hot-formed structural steel tubes for structural purposes.
EN 10219: Cold-formed welded structural steel pipes for structural purposes.
JIS G3452: Carbon steel pipes for general piping.
JIS G3454: Carbon steel pipes for pressure piping.
AS/NZS 1163: Cold-formed structural steel tubes and hollow sections for structural products and structural piping systems.
Key Parameters of Carbon Steel Pipe
Tube Size
The dimensional parameters of carbon steel pipe are critical to ensure proper installation and performance of the piping system.
Outside diameter (OD): The diameter of the outside of the pipe, is directly related to the pipe connection and layout.
Inside diameter (ID): the diameter of the inside of the pipe, which affects the flow rate and flow of fluids.
Wall thickness (WT): the thickness of the wall of the pipe, which is critical to the pressure tolerance and rigidity of the pipe.
Length (L): The pipe can be of fixed or random length.
Roundness and straightness: determine the installation quality of the pipe and the sealing of the connection.
Tube end type: The tube end can be flat, beveled, or threaded to accommodate different connection types.
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of carbon steel pipe determines its hardness, strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance.
Carbon (C): increases hardness and strength, but too much reduces toughness.
Manganese (Mn): increases strength and wear resistance while maintaining good toughness.
Silicon (Si): enhances elasticity and heat resistance.
Sulphur (S) and phosphorus (P): are usually regarded as impurities and need to be kept at low levels as they reduce toughness and weldability.
Other alloying elements (e.g. chromium, nickel, molybdenum): can improve specific mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical property parameters directly affect the stability of carbon steel pipe under service conditions.
Tensile strength: the ability of the material to resist fracture in tension.
Yield strength: the maximum stress to which the material is subjected before it begins to deform permanently.
Elongation: An indication of the ability of a material to deform plastically, the extent to which it can elongate before fracture.
Hardness: The ability of a material to resist localized indentation, often measured by Brinell, Rockwell, or Vickers hardness tests.
Impact test: An impact test performed at a certain temperature to evaluate the toughness of a material.
When selecting carbon steel tubes, these key parameters must be in accordance with the specific application requirements and the corresponding standards.
Carbon Steel Pipe Surface Coating
Surface coating protection for carbon steel pipe is an important means of preventing corrosion and extending pipe life. Different types of coatings provide different levels of protection and are suitable for different operating environments and conditions.
The following are some common types of surface coatings for carbon steel pipe:
Epoxy coatings: provide good adhesion and chemical resistance and are commonly used for corrosion prevention and underwater applications.
Polyurethane coatings: Provide excellent weathering and abrasion resistance and are used in externally exposed environments.
Zinc-rich coatings: Containing a high percentage of zinc powder, they provide cathodic protection and are suitable for marine and industrial environments.
Galvanizing: Provides cathodic protection by hot-dipping or electroplating zinc and is the traditional method of preventing corrosion.
Aluminum plating: provides superior protection to galvanizing under certain conditions, especially in high-temperature environments.
Polyethylene (PE) coating: Provides good chemical and impact resistance and is commonly used for underground piping.
Polypropylene (PP) coating: similar to PE coating but offers better performance at higher temperatures.
Cement mortar lining: Suitable for sewage and water supply pipes to prevent internal corrosion and fluid contamination.
Rubber lining: Provides physical protection and reduces corrosion and abrasion caused by fluids.
Each type of coating has its specific application scenarios, advantages, and disadvantages. A variety of factors including cost, construction conditions, life expectancy, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements need to be considered when selecting an appropriate coating.


Advantages of Carbon Steel Pipe
Carbon steel pipe offers a variety of advantages that make it the material of choice for many industrial applications.
1. Price advantages: Cheaper than stainless steel or alloy steel, it is the best choice for large projects and long-distance pipelines.
2. Mechanical strength: They have good mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and impact resistance. This means that it can withstand high pressures and harsh working environments.
3. Ease of processing: Easy to cut, weld, and shape for later installation and maintenance.
4. Good thermal conductivity: Carbon steel is a good conductor of heat and is suitable for applications such as heat exchangers and heating systems where efficient heat transfer is required.
5. High temperature resistance: It maintains its physical properties at higher temperatures and is suitable for environments that require high operating temperatures, such as steam systems.
6. Recyclability: It is a recyclable material that can be returned to the furnace for reuse at the end of the use week.
7. Abrasion resistance: The good hardness allows for good abrasion resistance when conveying abrasive materials and is, for example, widely used for material conveying in the mining and powder handling industries.
8. Compatibility: Compatible with many different types of connectors and fittings, with a wide range of accessories and easy sourcing.
Disadvantages of Carbon Steel Pipe
Although carbon steel pipes are widely used in numerous industrial applications due to their several advantages, they also have some disadvantages or limitations.
1. Easy to corrosion: Especially in wet or corrosive environments. Corrosion can thin the wall thickness of the steel pipe, increasing the risk of rupture and ultimately leading to leakage or failure.
2. Maintenance costs: In order to resist corrosion and extend their service life, carbon steel pipes may require additional protective measures such as coatings, linings, or cathodic protection systems. Regular maintenance and inspections are required throughout the life of the pipe, which adds to the total cost.
3. Unsuitable for use with certain chemicals: Carbon steel is sensitive to certain chemicals and may corrode faster under the influence of these chemicals. For example, carbon steel is susceptible to stress corrosion cracking in environments with high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide.
4. Temperature limitations: Although carbon steels can withstand a range of high temperatures, the mechanical properties of the steel deteriorate at very high temperatures, resulting in reduced material strength and creep (deformation from prolonged exposure to high loads).
5. Low-temperature embrittlement: At low temperatures, both toughness and brittleness are reduced, resulting in brittle fracture under impact.
6. Weight issues: Carbon steel pipes are heavier than other materials, such as plastics, and may result in additional requirements and costs for mounting and supporting structures.
7. Thermal expansion: Thermal expansion that occurs during temperature changes, especially in long-distance pipelines. This needs to be taken into account in the design and installation of pipelines to avoid stresses and deformations caused by temperature changes.
Selecting the right pipe for the requirements of a particular application and/or taking the appropriate protective measures are key to ensuring success.
Application of Carbon Steel Pipe
1. Oil and gas industry: Widely used in the transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products, both in long-distance pipeline transportation systems and in drilling and oil well pipelines.
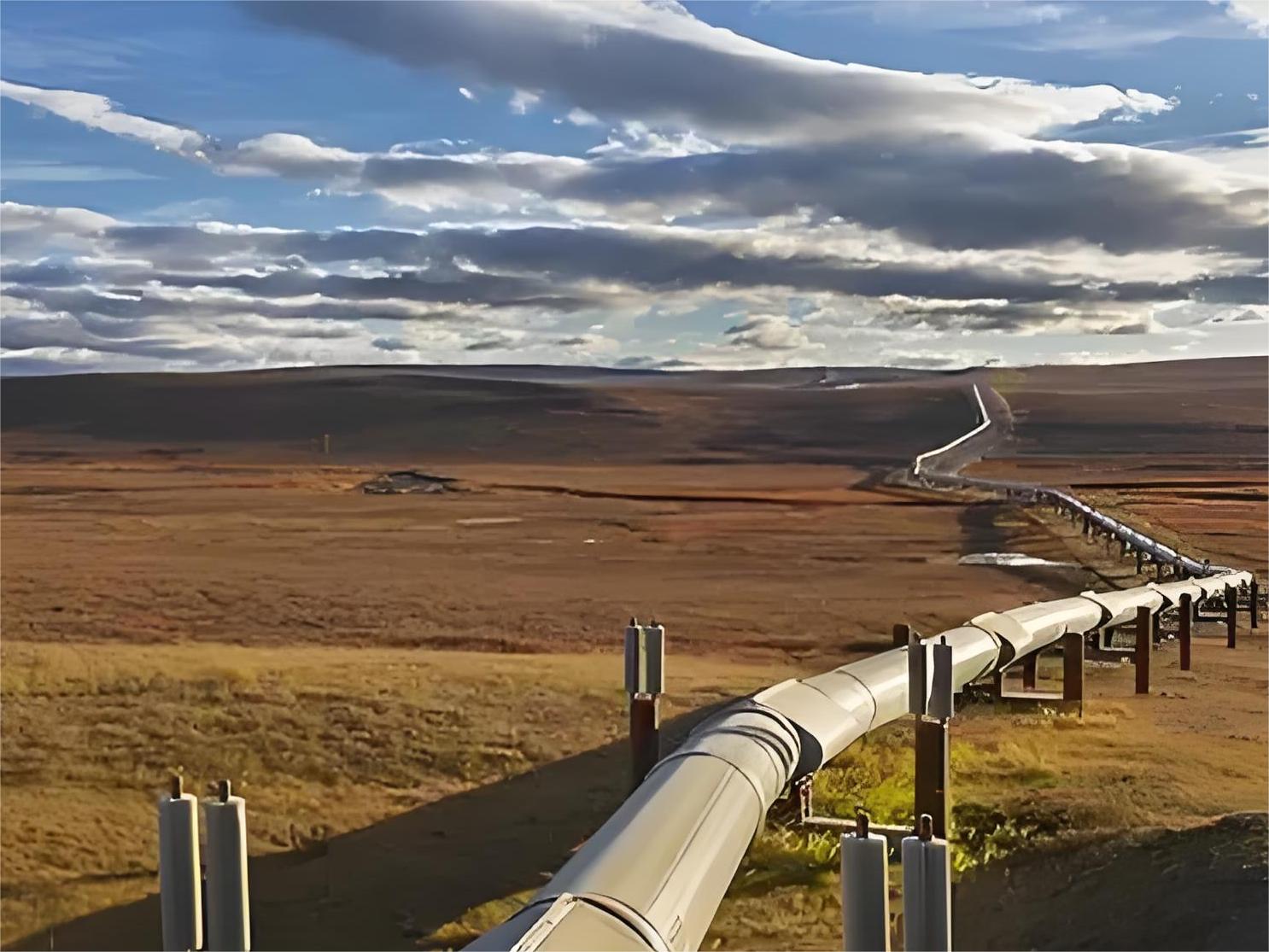

2. Chemical and petrochemical industries: These industries require pipes that are resistant to high temperatures and pressures to transport chemicals and fluids and therefore often use specially treated carbon steel pipes.
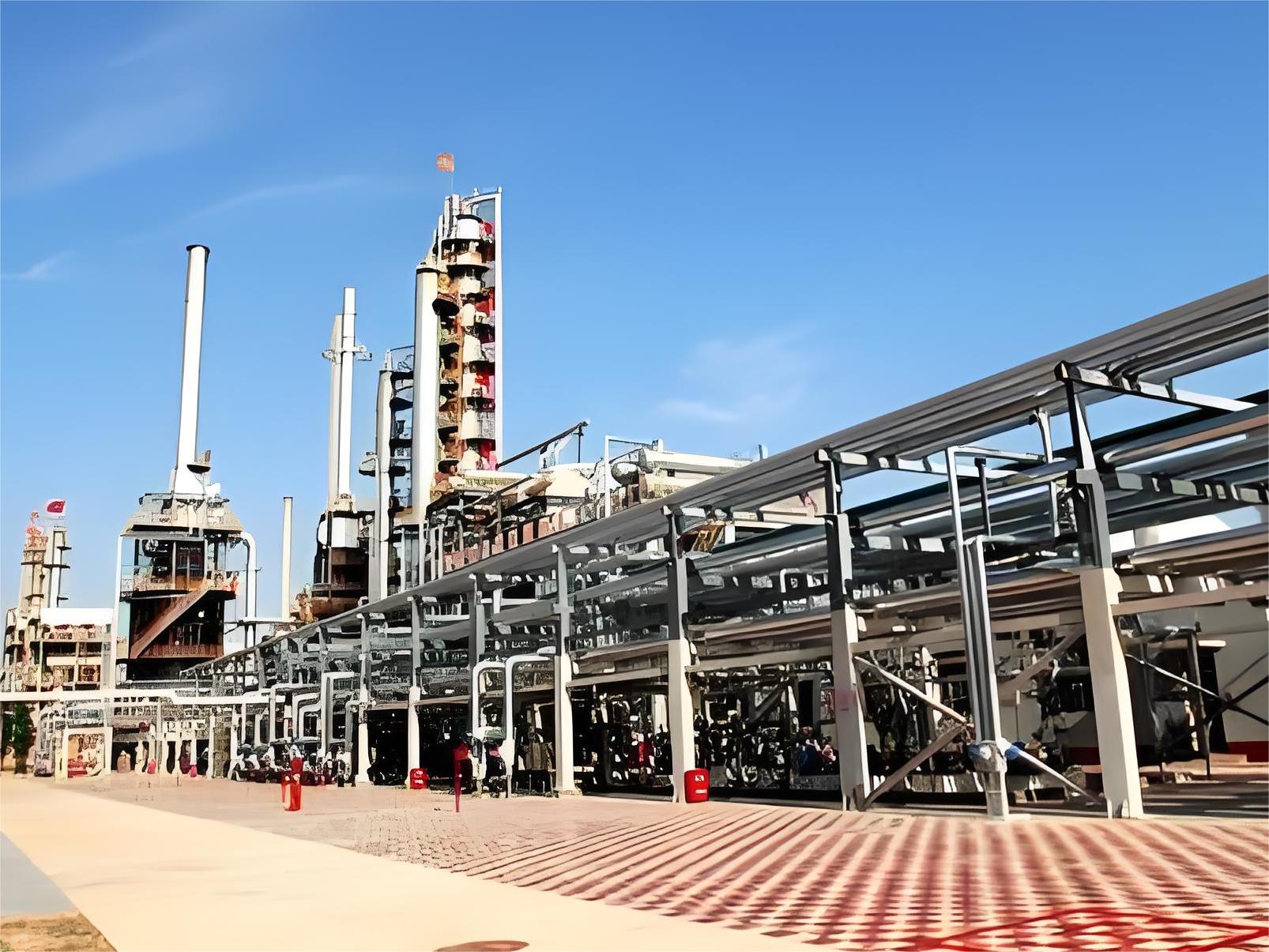

3. Manufacturing: Can be used to manufacture components for machinery and equipment, exhaust ducts, etc.
4. Building and construction: In the field of construction, they are used as the skeleton of building structures such as beams, columns, and other supporting structures. It is also used in the manufacture of scaffolding and other temporary structures.

5. Water and sewage: Widely used in piping systems for transporting water and sewage, steel pipes are often coated internally with a suitable layer of coating, which is used to protect the pipes from corrosion and prolong their service life.
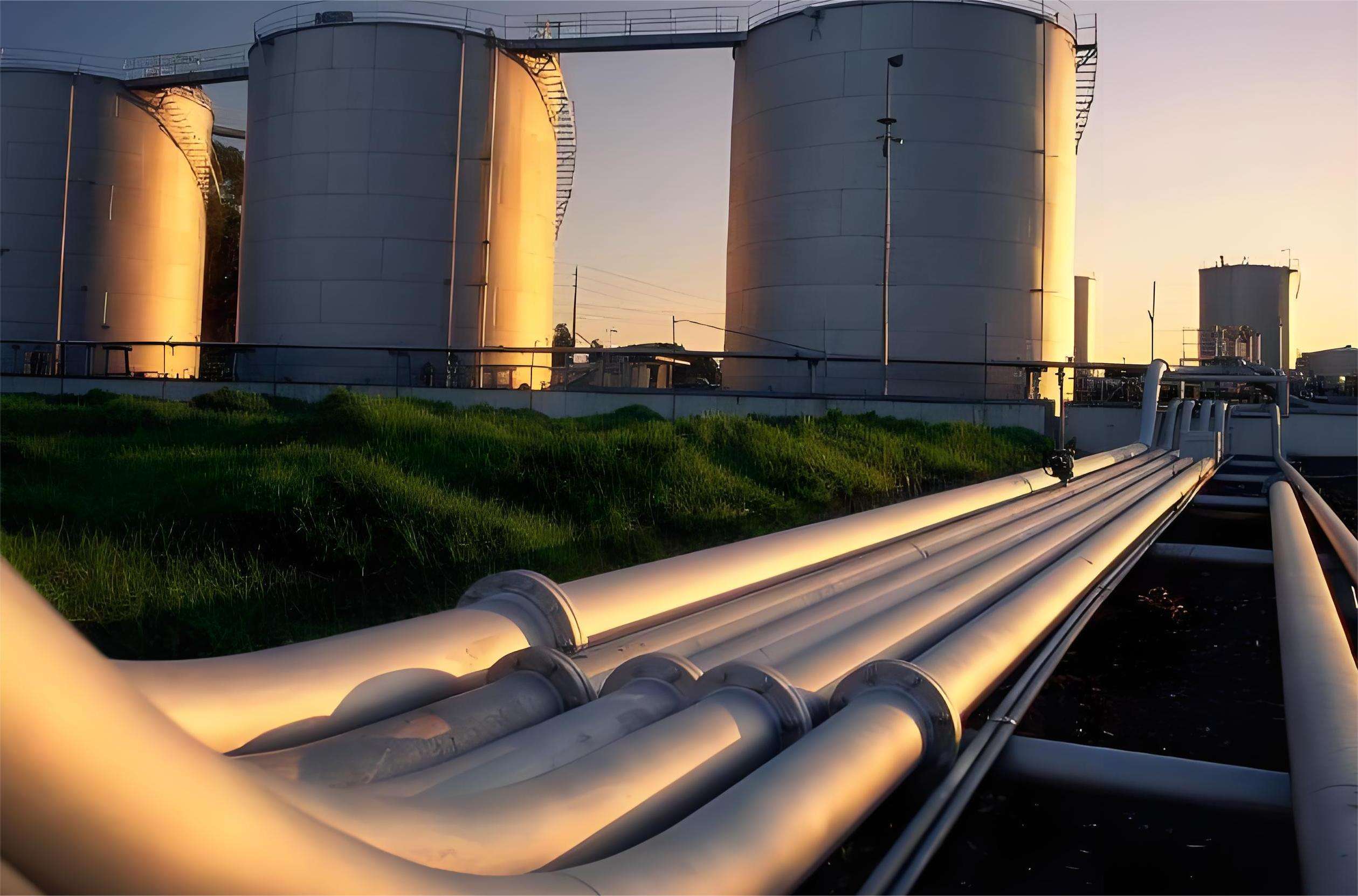

6. Energy industry: In power plants, they are used to transport high-temperature, high-pressure steam. They can also be used to make boilers and heat exchangers.
7. Heating and cooling systems: For transporting media or steam in central heating and air conditioning systems.
8. Marine industry: Used in ship construction for frame structures, drainage systems, and various other applications.
9. Thermal power stations: For steam and water transportation in thermal power stations.
10. Structures and engineering: Typically used to support structures for bridges, tunnels, subway systems, and large public facilities.
Carbon steel pipes are often selected based on their diameter, wall thickness, length, manufacturing process, and whether additional coatings or linings are required to resist corrosion. When applying them, it is critical to consider the temperature, pressure, and type of media in the working environment.
How to Choose a Reliable Carbon Steel Pipe Supplier
1. Qualifications and accreditations: Check that the supplier's products comply with international and domestic industry standards and that it has a quality management system certification (e.g., ISO 9001).
2. Product quality: Does the supplier provide test reports on the chemical composition and mechanical properties of raw materials and finished products. And understand the quality assurance measures, including inspection, testing, and quality control during the production process.
3. Production capacity: Assess whether the supplier's size and production capacity can meet the order requirements. Examine whether the production techniques and equipment used by the supplier are modernized to ensure product quality.
4. Market reputation: Consider the supplier's experience in the carbon steel pipe industry. Long-term business experience is usually associated with high reliability. Ask for feedback and comments from existing customers, especially regarding product quality and service satisfaction.
5. Service and support: Does the supplier provide good customer service, including quick response and problem-solving. Whether the supplier can provide professional technical support in the process of product selection, performance explanation, and installation.
6. Price and cost: Compare quotations from different suppliers to ensure that the price is in line with the market level and cost-effective. Watch out for possible hidden costs arising from transportation, packaging, possible delays, etc.
7. Delivery period: Whether suppliers are able to commit to and meet delivery deadlines, evaluate the supplier's logistics network to ensure that products can be delivered safely and on time.
8. After-sales service: Understand the supplier's after-sales service policy, such as returns and exchanges, quality objection handling, etc.
9. Company information survey: Utilize online resources to obtain additional information. For example, company websites, industry forums, social media, etc.
10. Site visits: If possible, you can visit the supplier's production plant, and production facilities in person.
11. Sample testing: Samples can be requested for testing to verify that the actual quality of the product meets the requirements.
Throughout the selection process, comprehensive evaluation and prudent judgment are key. Ensure that the supplier you choose is not just superior in terms of price, but is the best choice in terms of quality, reliability, and overall value.
About Us
Since its establishment in 2014, Botop Steel has become a leading carbon steel pipe supplier in Northern China, known for its excellent service, high-quality products, and comprehensive solutions. The company's extensive product range includes seamless, ERW, LSAW, and SSAW steel pipes, as well as pipe fittings, flanges, and specialty steels.
With a strong commitment to quality, Botop Steel implements stringent controls and tests to ensure the reliability of its products. Its experienced team provides personalized solutions and expert support, with a focus on customer satisfaction.
Tags: carbon steel pipe, suppliers, manufacturers, factories, stockists, companies, wholesale, buy, price, quotation, bulk, for sale, cost.
Post time: May-03-2024
