JIS G 3454 steel tubes are carbon steel tubes primarily suitable for use in non-high-pressure environments with outside diameters ranging from 10.5 mm to 660.4 mm and with operating temperatures up to 350 ℃.

Navigation Buttons
Grade Classification
Manufacturing Processes
Hot Dip Galvanizing -White Pipe
Chemical composition of JIS G 3454
Mechanical Properties of JIS G 3454
Flattening Test
Bending Test
Hydraulic Test or Non-destructive Test
Dimensional Tolerances
Pipe weight table and pipe schedules of JIS G3454
Appearance
Surface Coating of JIS G 3454
Marking
Applications of JIS G 3454 Steel Pipe
Our Related Products
Grade Classification
JIS G 3454 has two grades according to the minimum yield strength of the finished steel pipe.
STPG370, STPG410
Manufacturing Processes
Manufactured using an appropriate combination of tube manufacturing processes and finishing methods.
| Symbol of grade | Symbol of the manufacturing process | ||
| Pipe manufacturing process | Finishing method | Classification of zinc-coating | |
| STPG370 STPG410 |
Seamless: S Electric resistance welded: E |
Hot-finished: H Cold-finished: C As electric resistance welded: G |
Black pipes: pipes not given zinc-coating White pipes: pipes given zinc-coating |
Cold worked steel pipe shall be annealed after fabrication. If necessary, the Buyer may specify heat treatment of the welds of STPG 410 resistance welded steel pipe.
If resistance welding is used, the welds on the inner and outer surfaces of the pipe should be removed to obtain a smooth weld along the pipe contour. However, if it is difficult to remove the weld on the inner surface, the welded condition may be retained.
Hot Dip Galvanizing -White Pipe
For white pipe (pipes given zinc-coating), the surface of inspected black pipe (pipes not given zinc-coating) shall be cleaned by sandblasting, pickling, or other treatment prior to hot-dip galvanizing. Zinc for hot dip galvanizing shall be JIS H 2107 Grade 1 distilled zinc ingot or zinc of equal or better quality.
Other general requirements for galvanizing are in accordance with JIS H 8641.
Chemical composition of JIS G 3454
General items of analytical tests and methods of sampling and analysis shall be in accordance with JIS G 0404 item 8 (Chemical composition).
The analytical method shall be in accordance with JIS G 0320.
| Symbol of grade | C (Carbon ) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulfur) |
| max | max | max | max | ||
| STPG370 | 0.25% | 0.35% | 0.30-0.90% | 0.04% | 0.04% |
| STPG410 | 0.30% | 0.35% | 0.30-1.00% | 0.04% | 0.04% |
Mechanical Properties of JIS G 3454
The general requirements for mechanical testing are in accordance with JIS G 0404 Clause 7 (General Requirements) and Clause 9 (Mechanical Properties).
However, the method of specimen collection for mechanical testing shall be in accordance with JIS G 0404 Clause 7.6 (Specimen collection conditions and specimens), Type A.
Pipe testers shall perform tests in accordance with JIS Z 2241 and the tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation shall be in accordance with Table 3.
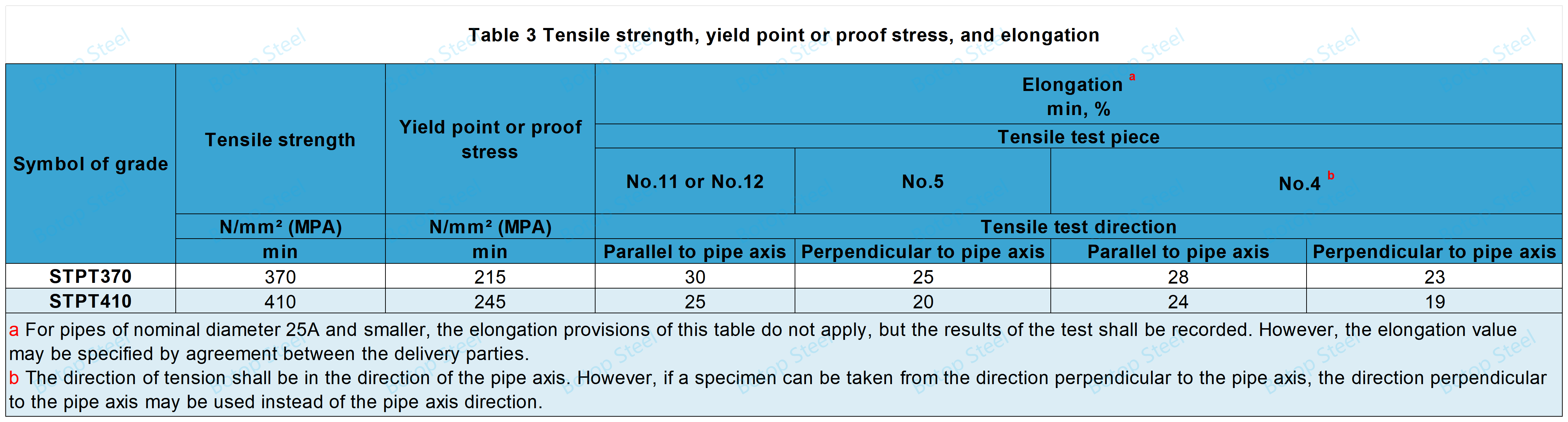
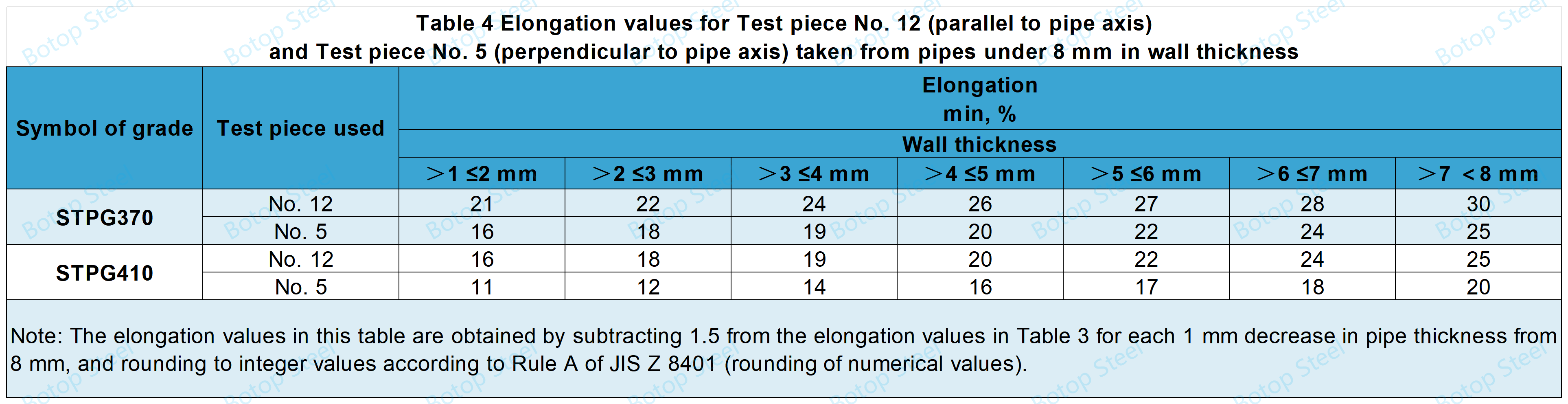
However, for tubes less than 8 mm thick, the elongation shall be in accordance with Table 4 for tensile tests using No. 12 or No. 5 specimens.
Flattening Test
The test temperature should be room temperature (5~35℃), the specimen is placed between two flat plates and compressed until the distance H between the plates is less than the specified value, when the specimen is flattened, observe whether there is a crack on the surface of the steel pipe sample block.
When H=2/3D, check the weld for cracks.
When H=1/3D, check for cracks in parts other than the weld seam.
Seamless steel pipe may be exempted from the flattening test, but the performance of the pipe must be in accordance with the provisions.
Bending Test
Applicable to pipes with outside diameter ≤ 40A (48.6mm).
The specimen shall not crack when bent at 90° with an inner radius of 6 times the outside diameter.
The buyer may specify a bending angle of 180 and/or an inner radius of 4 times the outside diameter of the pipe.
For resistance welded pipes, the weld seam shall be located approximately 90° from the outermost part of the bend.
Hydraulic Test or Non-destructive Test
All pipes must be hydraulically tested or non-destructively tested.
However, for white pipes, this is usually done before galvanizing.
Hydrotesting or non-destructive testing is an important means of piping quality control to ensure the safety and reliability of piping during installation and use.
Hydrostatic Test
Apply a higher-than-specified hydraulic test pressure to the pipe and hold it for at least 5 seconds to see if the pipe can withstand the pressure and if leakage occurs.
| Table 5 Minimum hydraulic test pressure | ||||||
| Nominal wall thickness | Schedule number: Sch | |||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 80 | |
| Minimum hydraulic test pressure, Mpa | 2.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 9.0 | 12 |
Non-destructive Testing
The ultrasonic test (UT) method shall be in accordance with JIS G 0582. However, a more stringent test than the UD classification of artificial defects may also be used instead.
Eddy's current test (ET) method shall be in accordance with JIS G 0583. However, it can also be replaced by a more stringent test than the EY Artificial Defects classification.
Of course, other non-destructive testing methods that meet the criteria can be chosen instead.
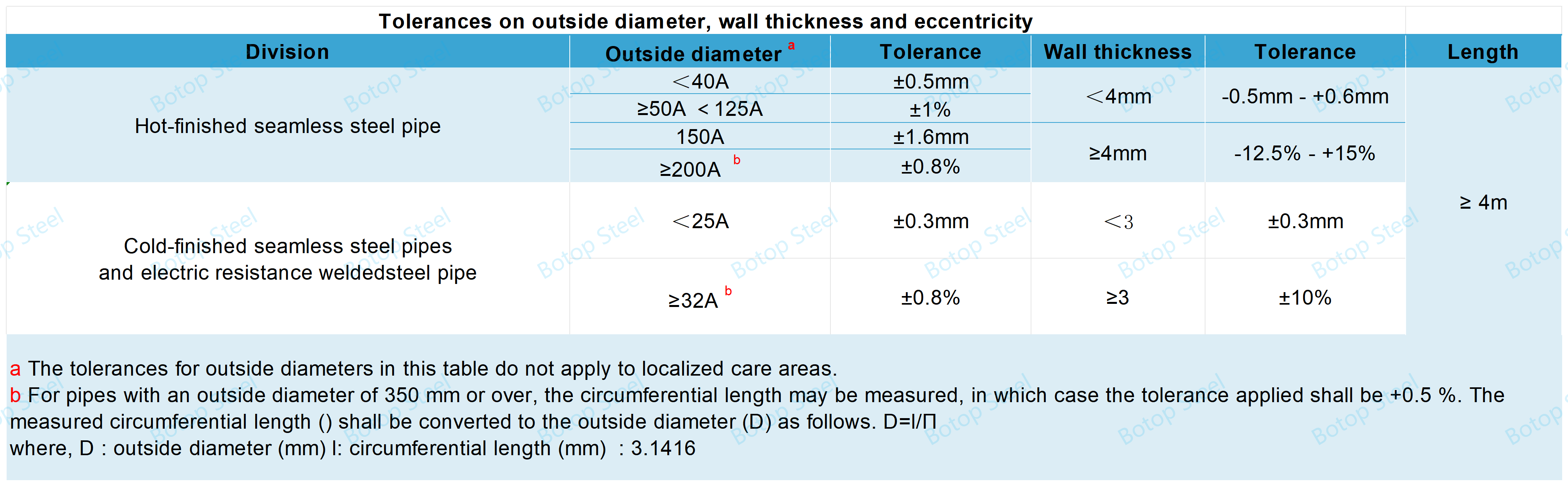
Dimensional Tolerances
Negative tolerances on the thickness of resistance-welded steel pipes apply only to resistance-welded steel pipe welds; positive tolerances do not apply.
Pipe weight table and pipe schedules of JIS G3454
Steel Pipe Weight Calculation Formula
W=0.02466t(D-t)
W: unit mass of pipe (kg/m)
t: wall thickness of pipe (mm)
D: outside diameter of pipe (mm)
0.02466: conversion factor for obtaining W
The above formula is a conversion based on the density of steel tubes of 7.85 g/cm³ and the results are rounded to three significant figures.
Steel Pipe Weight Table
Pipe weight charts play a very important role in the process of pipeline design, engineering, procurement, and construction, and are an indispensable and important reference in pipeline engineering.
Pipe Schedules
A pipe schedule is a table used to standardize pipe dimensions, usually to specify the wall thickness and nominal diameter of a pipe.
Schedule 10, 20, 30, 40, 60 and 80 in JIS G 3454.
Learn more about pipe weights and pipe schedules within the standardized.
Appearance
The pipe shall be basically straight and its ends shall be basically perpendicular to the axis of the pipe.
The inner and outer surfaces of the pipe shall be of good finish and free from defects unfavorable to use.
Surface treatment can be done by grinding, machining, and other methods to deal with surface defects, but the thickness after treatment is not less than the minimum thickness, and the shape of the pipe remains consistent.
Surface Coating of JIS G 3454
The internal and external surfaces of steel pipes can be coated with anticorrosive coatings, such as zinc-rich coatings, epoxy coatings, primer coatings, 3PE, and FBE.
Marking
Steel tubes that pass inspection shall be marked with the following information on a tube-by-tube basis. However, if the small outside diameter of the tubes makes it difficult to mark each tube individually, the tubes may be bundled and each bundle marked in an appropriate manner.
The order of marking is not specified. In addition, Certain items may be omitted by agreement between the parties to the delivery, provided that the product can be identified.
a) Symbol of grade
b) Symbol of the manufacturing process
The symbol of the manufacturing process shall be as follows. The dashes may be replaced with blanks.
Hot-finished seamless steel pipe: -S-H
Cold-finished seamless steel pipe: -S-C
As electric resistance welded steel pipe: -E-G
Hot-finished electric resistance welded steel pipe: -E-H
Cold-finished electric resistance welded steel pipe: -E-C
c) Dimensions, expressed by nominal diameter × nominal wall thickness, or outside diameter × wall thickness.
d) Manufacturer's name or identifying brand
Example: BOTOP JIS G 3454-S-H STPG 370 50A×SHC40 HEAT NO.00001
Applications of JIS G 3454 Steel Pipe
JIS G 3454 standard steel pipes have a wide range of applications in various industrial and construction fields, mainly used for conveying various fluid media.
Water supply systems: JIS G 3454 standard steel pipes can be used in municipal water supply systems, industrial water supply systems, etc. to transport clean tap water or treated water.
HVAC systems: These steel pipes are also commonly used in HVAC systems to convey cooling water or hot water.
Pressure vessels: JIS G 3454 steel pipes are also used in some pressure vessels and boilers
Chemical plants: These can be used to convey a variety of chemical media.
Oil and gas industry: although JIS G 3454 is mainly suitable for low-pressure transportation, it may also be used in some less demanding oil and gas industry applications.
We are a high-quality welded carbon steel pipe manufacturer and supplier from China, and also a seamless steel pipe stockist, offering you a wide range of steel pipe solutions!
Tags: JIS G 3454, STPG, SCH, carbon pipe, white pipe, black tube, suppliers, manufacturers, factories, stockists, companies, wholesale, buy, price, quotation, bulk, for sale, cost.
Post time: May-01-2024
