ASTM A500 and ASTM A513 are both standards for the production of steel pipe by the ERW process.
Although they share some manufacturing processes, they differ significantly in a number of ways.

Steel Type
ASTM A500: Standard Specification for Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and Shapes
ASTM A500 can only be carbon steel.
ASTM A513: Standard Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon and Alloy Steel Mechanical Tubing
ASTM A513 can be carbon steel or alloy steel.
Size Range
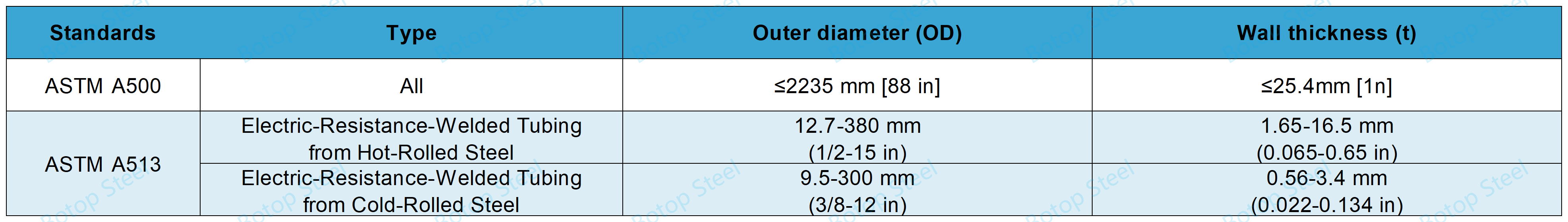
Manufacturing Process
ASTM A500 Manufacturing Process
The tubing shall be made by a seamless or welding process.
Welded tubing shall be made from flat-rolled steel by the electric-resistance-welding (ERW) process.
A500 is usually made from steel in the hot-rolled state, then cold-formed and welded.
Note: Flat-rolled refers to a metalworking process that is primarily applied to steel and other metallic materials. In this process, the metal starts in its original bulk form (e.g. ingot) and is flattened into sheets or coils through a hot or cold rolling process.
ASTM A513 Manufacturing Process
Tubes shall be made by the electric-resistance-welded process and shall be made from hot- or cold-rolled steel as specified.
Heat Treatment
ASTM A500 Heat Treatment
Tubes in the ASTM A500 standard do not normally require heat treatment. This is because ASTM A500 is intended primarily for structural use, where the emphasis is on adequate structural strength and toughness. These tubes are typically produced by cold forming and subsequent welding, using carbon steel material that already has some strength and toughness.
However, in certain specific cases, in order to achieve particular mechanical properties or to meet specific technical requirements, tubes and pipes of ASTM A500 may be subjected to normalizing or stress-relieving heat treatments, particularly where residual stresses are removed after welding.
ASTM A513 Heat Treatment
The ASTM A513 standard offers several types of tubing, some of which may be heat-treated to achieve desired mechanical properties.

NA (Not Annealed) - Not annealed; refers to steel tubing that has not been heat treated in the welded or drawn condition, i.e., it is left in its original condition after welding or drawing. This treatment is used for applications where no change in mechanical properties is required by heat treatment.
SRA (Stress Relieved Annealed) - Stress Relieved Annealing; this heat treatment is carried out at temperatures below the lower critical temperature of the material, with the main purpose of removing the internal stresses generated during the processing of the tube, thus improving the stability of the material and preventing deformation after processing. Stress-relieving annealing is usually used in the machining of precision parts to ensure dimensional and shape accuracy.
N (Normalized or Normalized Annealed) - Normalized or normalized annealing; heat treatment at temperatures above the upper critical temperature of the material by which the grain size of steel can be refined and its mechanical properties and toughness improved. Normalizing is a common heat treatment used to enhance the mechanical properties of a material to make it more suitable for higher working loads.
Chemical Composition and Mechanical Properties
ASTM A500 tubing is designed for structural purposes and has specific mechanical (tensile strength, yield strength, elongation) and chemical properties.
It is known for its good weldability and ductility and can be used in structures requiring high strength-to-weight ratios.
There are several different types of ASTM A513 tubing, each with its own mechanical and chemical properties for specific applications.
For example, Type 5 tubing is a drawn sleeve (DOM) product with tighter tolerances, better surface finish, and more consistent mechanical properties.
Main Application Areas
ASTM A500 is commonly used in structural applications such as buildings, bridges, and support components. It is used where higher strength and solid construction are required.
ASTM A513, on the other hand, is used in applications that require high-precision tolerances and surface finishes. Common uses include automotive parts and mechanical parts that may need to be fitted together with extreme precision.
Price
ASTM A500 products are generally less expensive due to the relatively less stringent dimensional accuracy requirements of the manufacturing process.
ASTM A513, especially Type 5 (DOM), can be more expensive due to the additional machining required for better accuracy and surface finish.
Therefore, the choice between these two types of steel pipe should be based on the specific needs of the project.
If the project requires structural strength and durability, ASTM A500 is a more appropriate choice. Whereas, for applications that require high precision and excellent surface condition, ASTM A513 may be preferred.
Tags: ASTM a500 vs a513, astm a500, astm a513, carbon steel tube.
Post time: May-08-2024
